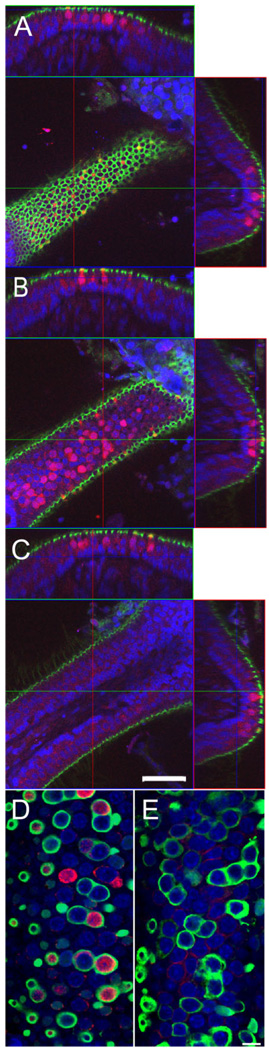
Figure 8.
BK channel expression in cristae ampullaris. A–C: A horizontal crista of a 3-week-old animal triple stained for actin (phalloidin; green), nuclei (NeuroTrace, blue) and BK (red) is shown. Optical confocal sections at different Z planes through a single crista are shown in the middle, and the reconstructed orthogonal sections along the XZ and YZ planes are shown on top and to the right of the XY plane, respectively. A: Confocal section through the top of the crista. Note the reticular appearance of the actin associated with tight junctions. BK-positive hair cells appear yellow in the center image due to the overlay of the green actin and red BK signal. B: Confocal section through the middle of hair cells at the apical portion of the crista. Note the numerous BK-positive hair cell bodies. C: No BK-positive hair cells are found at the lateral edges of the crista. Note the actin-positive hair bundles perpendicular to the edge of the crista. In A–C, the cross-sectional reconstructions above and to the right of the images further illustrate the exclusive localization of BK-positive hair cells to the apical portion of the crista. D: Confocal section through the apical portion of a horizontal crista of a 3-week-old animal triple stained for BK (red), calretinin (green), and NeuroTrace (blue). Note the calretinin-positive calyces associated with many of the BK-positive hair cells. E: Confocal section through the apical portion of a horizontal crista of an adult animal. Note the absence of BK-positive hair cells. Scale bar = 50 µm in A–C; 10 µm in D,E.