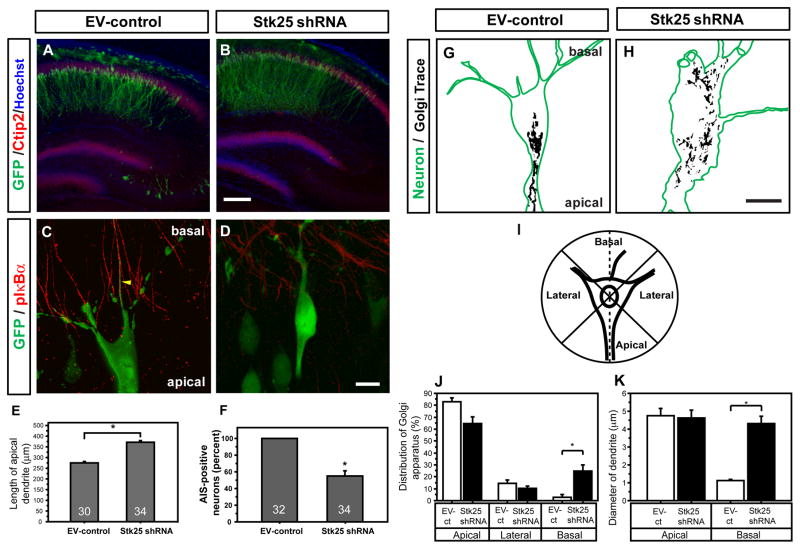
Figure 2. Stk25 regulates neuronal polarity during brain development.
A EV-control vector (GFP positive, green) electroporated at E16.5 in utero was expressed in Ctip2-positive (red), hippocampal-pyramidal neurons at P7. B Stk25 shRNA-expressing neurons (GFP positive) were appropriately positioned in the CA1 layer, and their apical dendrites extended further than EV-control. C GFP-expressing, EV-control transfected CA1 neurons had the typical pyramidal shape and phospho-IκBα- (red), GFP-positive (green) axon initial segments (Sanchez-Ponce et al., 2008; movie S1). D In contrast, a high percentage of strongly GFP-positive, Stk25 shRNA-expressing neurons were often misshapen and lacked axon initial segments (movie S1). E Quantification of apical dendrite length in EV-control and Stk25 shRNA hippocampi. F Quantification of the number of GFP-, Ctip2-positive pyramidal neurons that had axon initial segments (n indicated in bar.) G In EV-control neurons, the Golgi apparatus (trace of GRASP65 signal) is concentrated on the apical side of the neuron (movie S2). H In Stk25 shRNA-expressing neurons, the Golgi apparatus was broadly distributed throughout the neuron (movie S2). I Scheme used to determine Golgi distribution in J. J The Golgi distribution in apical, lateral (combined) or basal quadrants was quantified. K The diameter of the largest apical and basal processes was determined (*p <0.0005, Student’s t-test, n≥12, neurons from 3 animals). Bars B 200 μm; D, H 10 μm. Error bars indicate SEM in all figures.