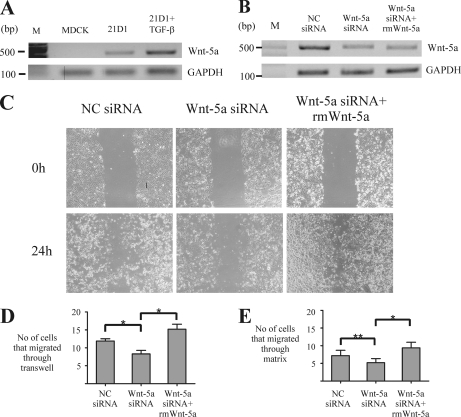
Fig. 4.
siRNA silencing of Wnt-5a attenuates 21D1 cell migration and invasion. A, transcript expression of Wnt-5a was not detected in MDCK cells by semiquantitative RT-PCR; however, transformation with H-Ras and stimulation with TGF-β induces Wnt-5a expression. B, expression of Wnt-5a in 21D1 cells is attenuated by RNA interference using siRNA duplexes targeting Wnt-5a. The addition of scrambled negative control (NC) siRNA did not affect Wnt-5a expression. Expression of Wnt-5a was reduced in 21D1 cells using transient siRNA transfection, and cell migration was assessed using the wound healing (C) and Transwell migration (D) assays. Both assays show that cell migration is significantly impeded when expression of Wnt-5a is reduced. However, cell migration is restored and even elevated with the addition of rm Wnt-5a (n = 2). E, the ability of 21D1 cells to invade through the matrix is decreased when expression of Wnt-5a is reduced using siRNA duplexes, although this reduction is not statistically significant (**). The invasive nature of 21D1 cells is rescued with the addition of recombinant Wnt-5a (n = 2). Error bars represent mean ± S.D. Significance is determined by a p value ≤0.05 using the Student's t test.