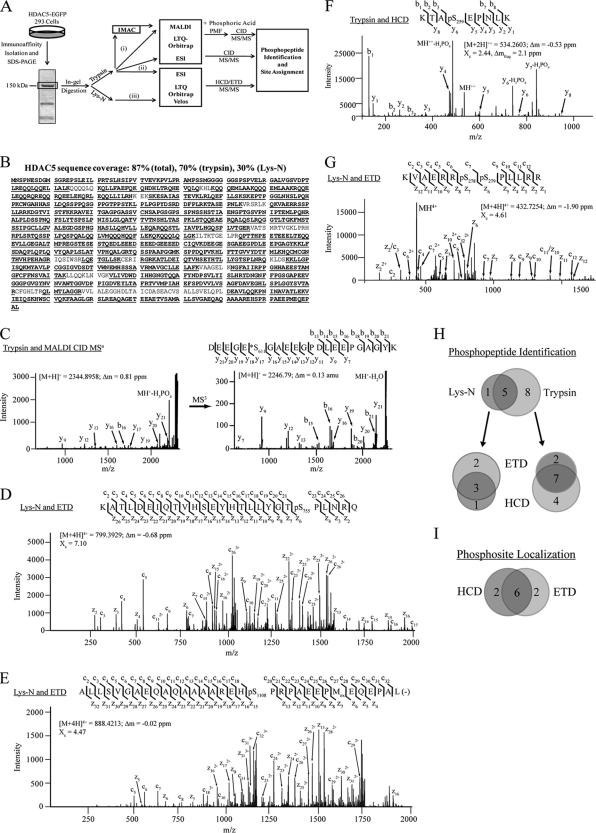
Fig. 2.
Combinatorial mass spectrometric approach allows a comprehensive view of in vivo phosphorylation on HDAC5. A, Workflow for phosphopeptide characterization of HDAC5 using immunoaffinity isolation, in-gel digestion, and complementary mass spectrometric approaches. Proteomics strategies employed include (i) MALDI-IMAC analysis, (ii) ESI-LC CID analysis, and (iii) ESI-LC HCD/ETD analysis. B, 87% sequence coverage of HDAC5, including unmodified and phosphorylated peptides, was obtained. C, MALDI CID MS/MS of tryptic phosphopeptide. Prominent neutral losses of phosphoric acid (H3PO4) and water were observed. MS3 fragmentation of the neutral loss species (M+H+- H3PO4) localized the phosphorylation site (Ser611) as a dehydroalanine, marked with *. (D and E) MS/MS ETD spectra corresponding to multiply charged Lys-N phosphopeptides. Phosphosites (Ser755 and Ser1108) were unambiguously localized, with nearly full sequence coverage of both c and z ion series. F, MS/MS HCD spectrum of tryptic phosphopeptide. Neutral losses of H3PO4 from the precursor and y6 and y7 fragment ions supported the phosphosite at Ser259. G, MS/MS ETD spectrum of a doubly phosphorylated peptide (Ser278 and Ser279) within the nuclear localization signal. For all mass spectra, the precursor m/z, charge state, mass error (Δm), and cross correlation score (Xc) are indicated. H, Venn diagram comparison of phosphopeptides identified from Lys-N and trypsin-digested HDAC5, and each as a function of fragmentation technique (ETD versus HCD). I, Venn diagram of the number of phosphosites unambiguously localized by HCD and ETD. Representative annotated, mass labeled phosphopeptide spectra are included in Supplemental Fig. S2.