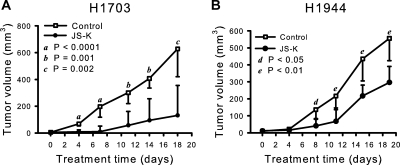
Fig. 2.
JS-K significantly reduced growth of NSCLC cells in vivo. JS-K was administered intravenously at 6 μmol/kg, three times a week for 3 weeks, and tumors were measured with a caliper. Growth of both cell lines, JS-K-sensitive H1703 (A) and over 10-fold less sensitive H1944 (B), was inhibited. Values are medians, and the relevant 95% confidence interval bars are shown (Mann-Whitney test). Letters indicate the significance of the differences between JS-K-treated and control mice at each time point. The treatment did not affect body weights. The average body weight for all mice was 22.7 ± 0.25 g (mean ± S.E.) at the beginning of the experiment. At the termination, the average weights of the control groups were 24.57 ± 0.88 g (n = 11) and 24.41 ± 0.57 g (n = 13), for H1703 and H1944 xenograft studies, respectively. The weights of JS-K treated animals were 24.92 ± 0.39 g (n = 9) and 24.42 ± 0.56 g (n = 11), for the H1703 and H1944 xenograft groups, respectively.