Figure 4.
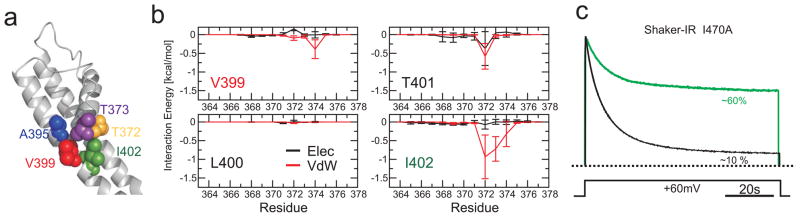
A common gate coupling mechanism in K+ channels. a. Structural representation of the interface between the inner bundle gate (S6) and the pore helix in the Kv 1.2 pore domain (2R9R) with key amino acid side chains shown as van der Waals spheres (Equivalent KcsA/Kv 1.2 positions: Met 96/Ala391, blue; Ile100/Val399, Red; and Phe103/Ile401, green; T74/T373, yellow; T75/T374, purple). b. Interaction free energies of selected Kv1.2 residues in TM2 (equivalent to those in KcsA) with individual side chains from residues in the pore helix. c. Equivalent role of Ile470 in gate coupling in Shaker. Representative Cut-open oocyte voltage clamp traces obtained from N-type inactivation-removed Shaker (Shaker-IR), black trace and the mutation I470A (green trace) expressed in Xenopus oocytes (n=5 for I470A). Currents were normalized to the peak current.