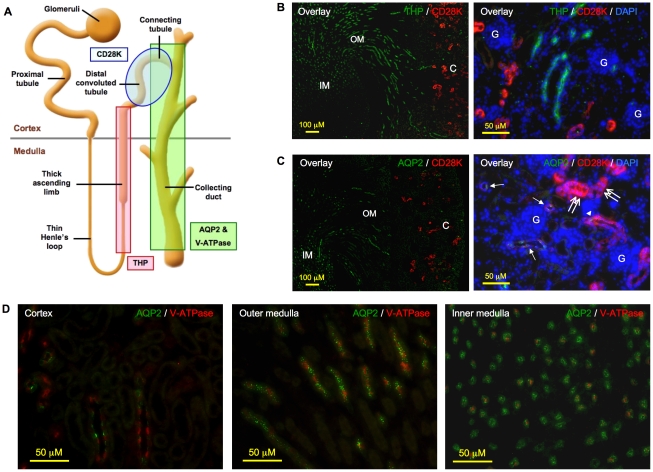
Figure 4. Characterization of antibodies for their specificity in labeling nephron and collecting ducts.
A. Schematic representation of nephron and collecting ducts. Tamm-Horsfall protein (THP), calbindin D28K (CD28K), aquaporin 2 (AQP2) and vacuolar H+-ATPase B1 (V-ATPase) antibodies were used to identify thick ascending limbs, distal convoluted tubules, as well as principal cells and intercalated cells of collecting ducts, respectively. B. Left panel (merged image): CD28K signal (red) was observed only in the cortex, whereas THP signal (green) was detected in both cortex and outer medulla, but not in the deep inner medulla. Original magnification was 100×. Right panel (merged image): CD28K (red) and THP (green) signals were mutually exclusive. Original magnification was 400×. C. Left panel (merged image): CD28K (red) was detected only in the cortex whereas AQP2 (green) was observed in the outer medulla and inner medulla. Original magnification was 100×; right panel (merged image): distal convoluted tubules stained exclusively and intensely for CD28K (double arrow); tubules stained positive for both CD28K and AQP2 were the connecting tubules (arrowhead) whereas those showing weak or negative CD28K but a positive AQP2 signal were the cortical collecting ducts (arrow). Original magnification was 400×. D. Principal cells and intercalated cells that stained positive for AQP2 (green) and V-ATPase (red), respectively, co-localized to the same tubules in the cortex, outer medulla and inner medulla. Original magnification was 400×. No specific signal was noted on sections incubated with non-immune IgGs in place of primary antibodies (data not shown). Shown here are kidney paraffin sections of a 2-week-old mouse. Nuclei were visualized with DAPI (blue) counterstaining. C: cortex; OM: outer medulla; IM: inner medulla; G: glomeruli.