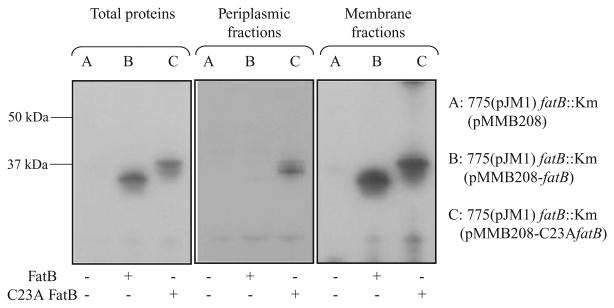
Fig. 6.
Western blot detection of FatB in cell fractions of V. anguillarum carrying either the wild-type FatB or C23A FatB. Periplasmic proteins were extracted as described by Wunderlich and colleagues (1993) with some minor modifications. Briefly, an exponential phase bacterial culture in CM9 minimal medium with 10 μg ml−1 Cm and 0.5 mM IPTG was centrifuged. The pellets were washed with CM9 minimal medium and resuspended in 2 ml BBS/EDDA (200 mM boric acid/NaOH, pH 8.0, 160 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA) per gram cell. The suspension was incubated for 45 min at 4°C with gentle agitation, and centrifuged (27 000 g, 1 h, 4°C) to pellet the spheroplasts. The supernatant containing periplasmic proteins was carefully transferred into new tubes. To obtain total protein the bacterial cells prepared as described above were resuspended into 10 mM Tris buffer (pH 7.6), sonicated 5 × 5 s and centrifuged at 15 000 r.p.m. at 4°C for 5 min. Supernatants were transferred into new tubes and used as total proteins. Membrane proteins were obtained by centrifuging the total proteins for 1 h at 30 000 g, and after resuspension this step was repeated. The presence of FatB or C23A FatB in the periplasm fractions and in total proteins was determined by Western blotting using anti-FatB serum.