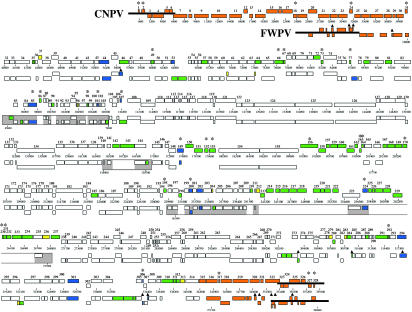
FIG. 1.
Comparative ORF map of CNPV and FWPV genomes. CNPV ORFs (top) are numbered from left to right based on the position of methionine start codons. ORFs transcribed to the right in each virus are located on top relative to those transcribed to the left; CNPV and selected FWPV genome positions are indicated below each virus. CNPV ORFs (top) are manually aligned with FWPV ORFs (bottom). Colored ORFs indicate differences between CNPV and FWPV: ORFs used to introduce gaps or lacking discernible orthologous sequence in the other virus are marked in green; nonhomologous ORFs in similar genomic positions are marked in blue; ORFs severely disrupted in the opposite virus are marked in yellow; and, due to extensive variability, ORFs in terminal regions marked in orange are unaligned. CNPV ORFs lacking discernible homology to any FWPV ORF are marked above with an asterisk; FWPV ORFs lacking discernible homology to any CNPV ORF are marked above with a triangle. Thick black bars at genomic termini represent ITRs. Boxed regions indicate novel coding regions at junction sites of major genome rearrangements previously identified in FWPV (2), with white indicating gaps between grey sequence.