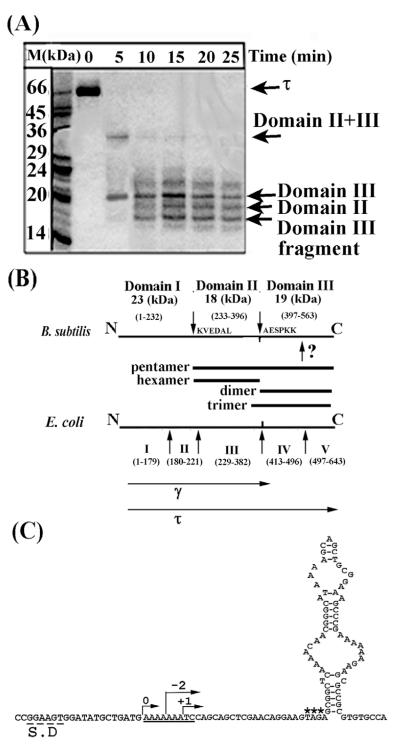
Figure 1.
Domain organisation of the B. subtilis τ protein. (A) An SDS-PAGE gel showing proteolytic fragments of τ produced by limited proteolysis with papain over time. Arrows indicate the identified domains, as shown. (B) Diagrams showing the papain cleavage sites and comparing the domain organisation of the B. subtilis and E. coli τ proteins. Bars indicate all the domains that were constructed and purified. The γ and τ proteins are indicated. The unidentified papain site within domain III is indicated by a question mark. The molecular mass and apparent oligomerisation states of the domains are indicated. (C) Sequence elements in the B. subtilis dnaX gene that may mediate a translational frameshift event. The Shine–Dalgarno sequence is labelled S.D, the translational slippage signal is underlined, asterisks label the stop codon and a potential stem-loop structure is shown immediately downstream from the stop codon. Arrows indicate the correct frame 0 and −2, +1 frames that will result in premature termination.