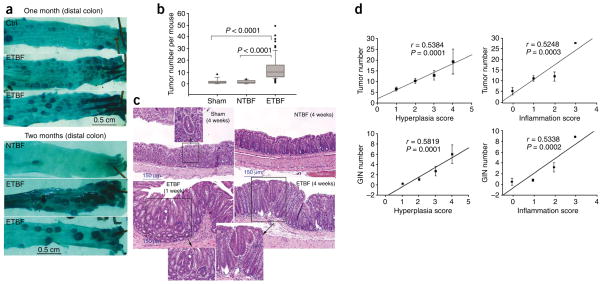
Figure 1.
ETBF stimulates colonic inflammation and enhances colonic tumor formation in Min mice. (a) Methylene blue–stained representative samples of distal colons of sham control, NTBF-colonized and ETBF-colonized mice showing thickened mucosal folds and excess tumors, visualized in mice colonized with ETBF for 1–2 months. (b) Distribution of visible tumor numbers detected in sham control, NTBF- or ETBF-colonized mice at 4–6 weeks after inoculation. Tumor distributions are shown as box-and-whisker plots. n = 14, 10 or 75 for sham control, NTBF or ETBF, respectively. (c) Distal colon histopathology of sham control and NTBF-colonized mice at 4 weeks and ETBF-colonized mice at 1 week and 4 weeks after inoculation. Insets show GIN foci in sham and ETBF-colonized mice. (d) Linear regression analysis of histological scores of ETBF-colonized colons for inflammation and hyperplasia versus visible colon tumor formation or GIN foci. Error bars represent means ± s.e.m.