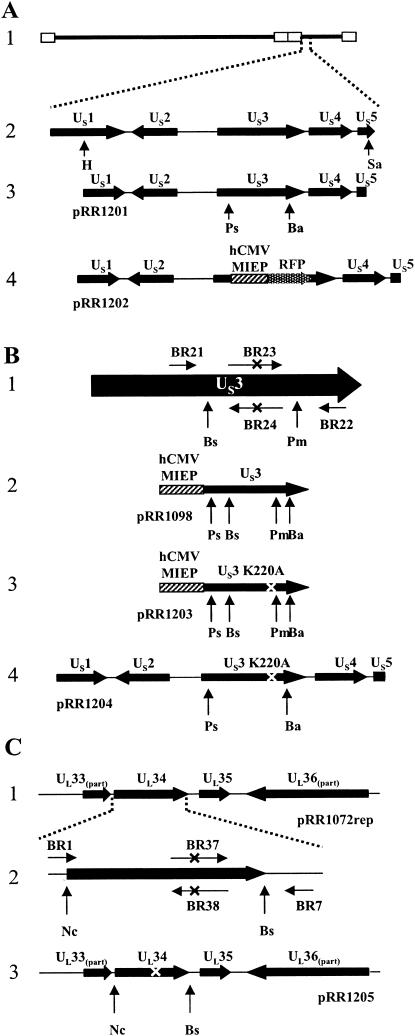
FIG. 1.
Construction of US3 and UL34 mutant plasmids. (A) Structure 1, schematic representation of the HSV-1(F) genome. Open rectangles indicate inverted repeats. Structure 2, HSV-1(F) genome expanded to show the arrangement of the US1 to US5 ORFs. Restriction sites used for construction of plasmid pRR1201 are indicated. Structure 3, arrangement of HSV-1 ORFs contained on plasmid pRR1201, showing restriction sites used for deletion of the US3 ORF. Structure 4, gene arrangement of US3 deletion plasmid pRR1202. US3 sequences were replaced with an hCMV-MIEP-RFP expression cassette. (B) PCR-based mutagenesis of the US3 protein. Structure 1,schematic representation of the US3 ORF (horizontal arrows represent PCR primers); structure 2, diagram of the US3 expression cassette of plasmid pRR1098; structure 3, diagram of the K220A US3 expression cassette of plasmid pRR1203; structure 4, diagram of the HSV-1 sequences of plasmid pR1204. For all structures, “X” indicates the position of the K220A mutation and generated PvuII restriction site and vertical arrows represent restriction sites used for cloning. (C) PCR-based mutagenesis of the UL34 protein. Structure 1, arrangement of HSV-1 ORFs contained on plasmid pRR1072rep. Structure 2, expanded diagram of the UL34 ORF. Horizontal arrows represent PCR primers and “X” indicates the position of the T195A/S198A mutation and generated SacI restriction site. Also shown are restriction sites used for cloning of the mutation-containing PCR product. Structure 3, arrangement of the HSV-1 ORFs contained on plasmid pRR1205. Restriction sites used for cloning are indicated and “X” indicates the position of the introduced mutation. Restriction enzyme abbreviations: Ha, HindII; Sa, SacI; Ps, PstI; Ba, BamHI; Bs, BspEI; Pm, PmlI; Nc, NcoI.