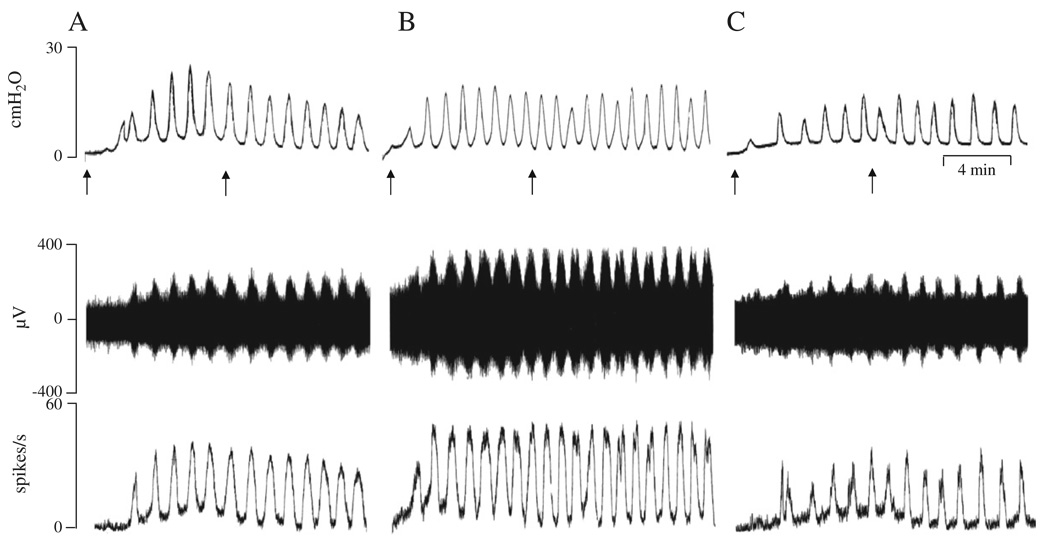
Fig. 1.
Enhancement of pelvic afferent nerve firing during bladder filling and after intravesical administration of oxo-M. The top traces represent bladder contractile activity measured as intravesical pressure, the middle traces represent pelvic afferent nerve activity and the bottom traces represent ratemeter recording of afferent firing (spikes/s). All records were obtained in the same preparation with 30–60 min periods between recordings. A: Control recording during bladder distension induced by intravesical infusion of Krebs solution at the rate of 0.04 ml/min for 8 min. Arrows indicate the start and end of infusion. B: Recording during intravesical infusion of 50 µM oxo-M. This preparation had also received an intravesical infusion of 25 µM oxo-M 40 min prior to this recording. C: Intravesical infusion of 50 µM oxo-M in combination with 5 µM AMN after pretreatment with 0.3 ml AMN (5 µM) for 10 min. Horizontal calibration represents 4 min.