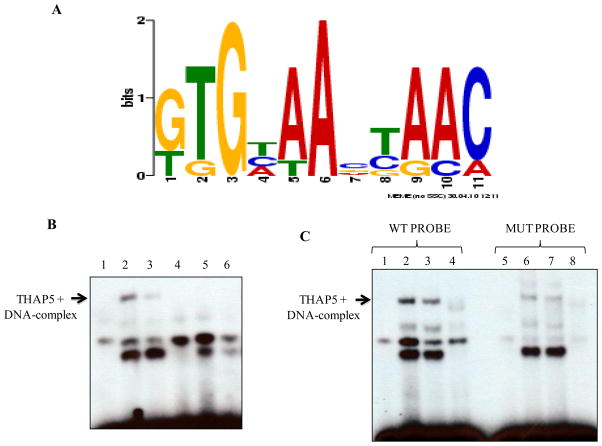
Fig. 3.
THAP5 recognized a specific DNA sequence. A, Identification of a consensus DNA-binding site for THAP5. This consensus sequence was created from a pool of 25 independent THAP5 bound oligonucleotides recovered at the end of 7 rounds of selection. The DNA sequences were analyzed by the motif-discovery program MEME. B, Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay showing THAP5 binding to the consensus DNA sequence. Lane 1, control (no extract); lane 2, MeWo nuclear extract; lane 3, MeWo extract with anti-THAP5 antibody; lane 4, NIH 3T3 extract; lane 5, MeWo extract plus 100 molar excess of cold THAP5 specific probe (WT) and lane 6, MeWo extract plus 100 molar excess of mutant probe incubated with 32P labeled wild type probe. C, Specificity of THAP5 Binding. First four lanes show THAP5 binding to the labeled WT probe. Lane 1, control (no extract); lane 2, MeWo nuclear extract; lane 3, MeWo extract with anti-THAP5 antibody; lane 4, NIH 3T3 extract. Lanes 5–6 show reduced binding of THAP5 to the labeled Mutant probe. Lane 5, control (no extract); lane 6, MeWo nuclear extract; lane 7, MeWo extract with anti-THAP5 antibody; lane 8, NIH 3T3 extract.