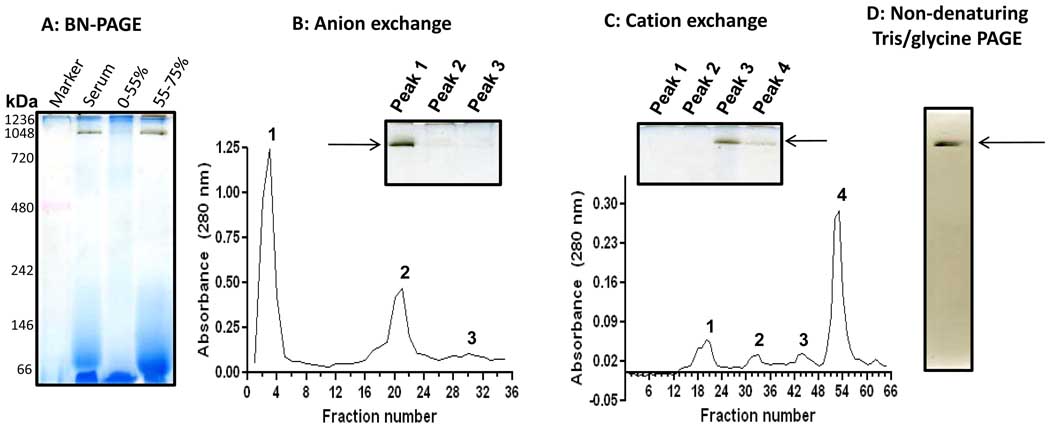
Fig. 6.
In-gel detection of human serum esterase activity following (NH4)2SO4 fractioning and ion exchange chromatographies. (A) BN-PAGE activity staining after (NH4)2SO4 fractionations. The serum was 10× diluted with Tris-HCl buffer (50 mM, pH 7.4) and then 55% saturated by the addition of solid (NH4)2SO4 (stirring at 4°C for1 hour). The mixture was centrifuged at 12,000 g for 10 min. The resulting supernatant was then 75% saturated by solid (NH4)2SO4. After incubation and centrifugation under the same conditions as described above, the pellet resulting from the 55–75% (NH4)2SO4 saturation was collected for gel analysis and further purification. (B) Anion exchange chromatography of the pellet fraction resulting from 75% (NH4)2SO4 saturation. Columns (Q Sepharose Fast Flow) were pre-equilibrated with 50 mM sodium acetate (pH 5.6) and eluted with step gradient of NaCl (20 mM increment/step) in the same buffer as described in the text. (C) Cation exchange chromatography of peak 1 fraction from B. The column (SP Sepharose Fast Flow) was pre-equilibrated with 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.6) and eluted with step gradient of NaCl (20 mM increment/step). For both B and C, the insets show in-gel activity staining of band G esterase activity using BN-PAGE. (D) In-gel esterase activity staining after Tris/glycine gel analysis (7.5% resolving, 4% stacking); the band was derived from BN-PAGE gel shown in the inset panel of C.