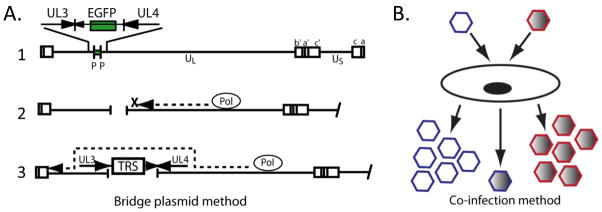
Figure 3.
New strategies for the rapid construction of novel, replication-competent HSV-1 vectors. A. The “bridge plasmid” method, in which the parent viral DNA contains unique restriction sites flanking the existing marker gene (line 1). The viral DNA is digested with the corresponding restriction enzyme, creating a site-specific gap in the viral DNA (line 2). Digested viral DNA is co-transfected with a plasmid that provides a “bridge” for the DNA polymerase to continue replication through the gap (line 3). B. The co-infection method, in which two parent viruses are used to co-infect permissive cells, and recombinant viruses expressing genes contributed from both parent viruses are selected.