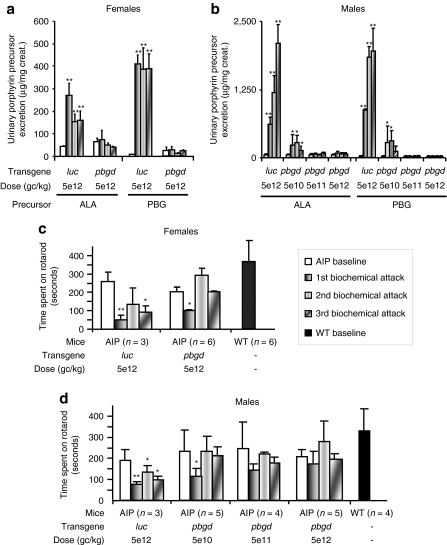
Figure 1.
Therapeutic efficacy of the rAAV2/8-hPBGD vector in AIP mice. Porphyrin precursor excretion [(a) females, (b) males] and motor coordination [(c) females, (d) males] were determined in mice before (baseline) and after biochemical induction of porphyrin precursors with increasing doses of phenobarbital for four consecutive days. Motor coordination was determined by the time that mice can stay on a rotating dowel turning at a positive acceleration. The first bar is baseline; the second bar represents measurements performed 15 days after the administration of a respective dose of rAAV2/8 vector and after phenobarbital administration. The third and forth bars show the same procedure performed 28 and 90 days after respective dose of gene therapy, respectively. Panels c and d have extra bars corresponding to baseline values from noninjected wild-type mice. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for comparison of means before and after phenobarbital administrations. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 versus baseline values in each group. AIP, acute intermittent porphyria; ALA, δ-aminolevulinic acid; PBG, porphobilinogen; rAAV, recombinant adeno-associated virus; WT, wild type.