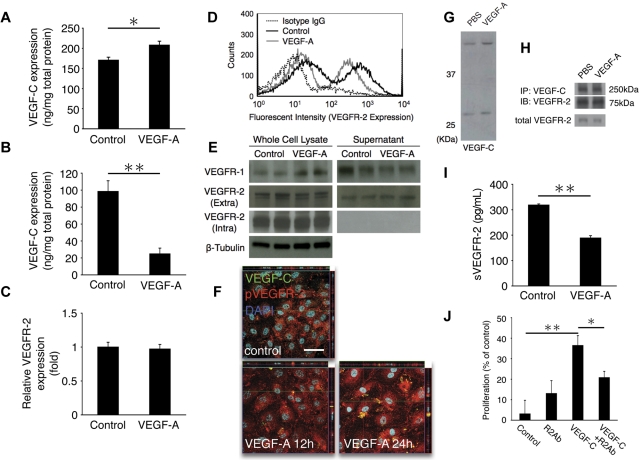
Figure 6.
Regulatory role of VEGFR-2 in VEGF-A–induced lymphangiogenesis. (A-B) VEGF-C expression with VEGF-A stimulation in whole cell lysates (A) and supernatant (B) of HUVECs, measured with ELISA (n = 4 [A] and 8 [B]). (C) VEGFR-2 mRNA level at 24 hours after VEGF-A stimulation is similar with control. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of VEGFR-2 expression in normal and VEGF-A–treated HUVECs, showing R2 down-regulation with VEGF-A stimulation at 24 hours. (E) Western blots of VEGFRs expression in whole cell lysates and supernatants of HUVECs with or without VEGF-A (24-hour treatment). (F) Confocal images of immunocytochemistry of phospho-VEGFR-2 (red) and VEGF-C (green) with or without VEGF-A stimulation (12 and 24 hours) in HUVECs. Arrows indicate pVEGFR-2/VEGF-C complex in the cytoplasm. Bar, 50 μm. (G) Representative Western blot samples from untreated and VEGF-A–treated HUVECs with α-VEGF-C Ab, showing up-regulation of precursor and secreted form of VEGF-C with VEGF-A. (H) Immunoprecipitated (IP) with VEGF-C and immunoblotted with VEGFR-2 Ab. tVEGFR-2 shows total VEGFR-2 without IP. (I) Soluble VEGFR-2 expression in VEGF-A–stimulated supernatant of HUVECs, measured with ELISA (n = 4). (J) VEGF-C–induced proliferation of HUVECs treated with IgG or VEGFR-2 Ab. Proliferation was measured at day 2 using the MTS assay (optical density at 490 nm). *P < .05; **P < .01.