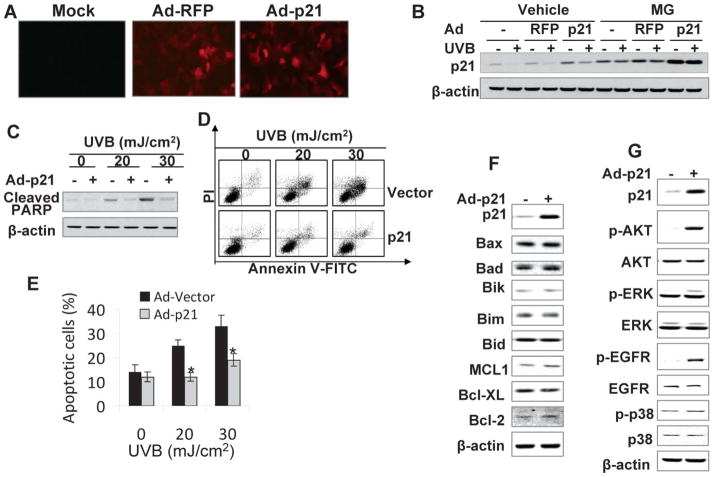
Fig. 6.
Reconstituting p21 protein levels inhibits UVB-induced apoptosis. (A) HaCaT cells were infected with adenoviral vectors expressing red fluorescent protein (RFP) (Ad-RFP) only, p21 and RFP (Ad-p21), or mock infected without viruses. Fluorescence showed efficient adenoviral infection and expression of RFP. (B) Cells were infected as in A and then exposed to UVB radiation (20 mJ cm−2). Cells were treated with or without MG following UVB radiation. The p21 protein levels were determined at 1.5 h upon UVB exposure. (C) Cells were infected as in A and then exposed to apoptosis-inducing UVB radiation (20 or 30 mJ cm−2). Cleaved PARP (PARP), an apoptosis marker, was determined at 6 h post-UVB. (D) Cells were infected and exposed to UVB as in B. Apoptosis was determined and quantified using Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide staining followed by flow cytometric analysis. (E) Percentage (%) of apoptotic cells (Annevin V positive) from histograms in D. *, p < 0.05; significant differences from UVB-irradiated vector-infected cells. (F) Immunoblot analysis of p21, Bax, Bad, Bik, Bim, Bid, MCL1, Bcl-XL, Bcl-2, and β-actin in HaCaT cells infected with an adenoviral vector expressing RFP alone or p21-RFP. (G) Immunoblot analysis of p21, p-AKT (serine 473), AKT, p-ERK, ERK, p-EGFR (Tyrosine 1197), EGFR, p-p38, p38, and β-actin in cells as in F.