Figure 7. Tau Acetylation Is Elevated under Pathological Conditions.
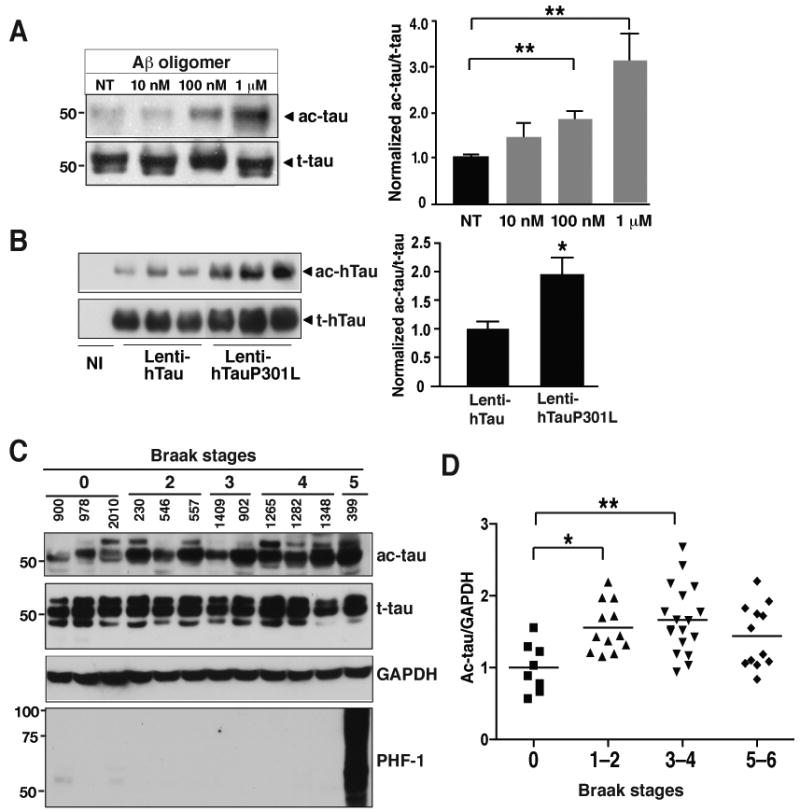
(A) Tau acetylation was increased by low levels of Aβ oligomers in primary cortical neurons (DIV=11). n=5 from 3 experiments. **, P=0.003 (one-way ANOVA and Tukey-Kramer posthoc test).
(B) Tau acetylation was associated with familial MAPT mutations in primary neurons (DIV=13). Ac-tau/t-tau levels in neurons infected with Lenti-hTauwt were set as 1. n=9 from three experiments. *, P=0.013 (unpaired t test).
(C) Representative western blots showing levels of ac-tau, t-tau, and hyperphosphorylated tau in human brains (Bm-22, superior temporal gyrus) at different Braak stages (0–5).
(D) Ac-tau levels were elevated in patients with mild (Braak stages 1–2) to moderate (Braak stages 3–4) levels of tau pathology. n=8–18 cases/Braak range. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01, one-way ANOVA Tukey-Kramer posthoc analyses. See Table-S2 for the patient information. Values are means±SEM (A, B, D).
