Figure 2.
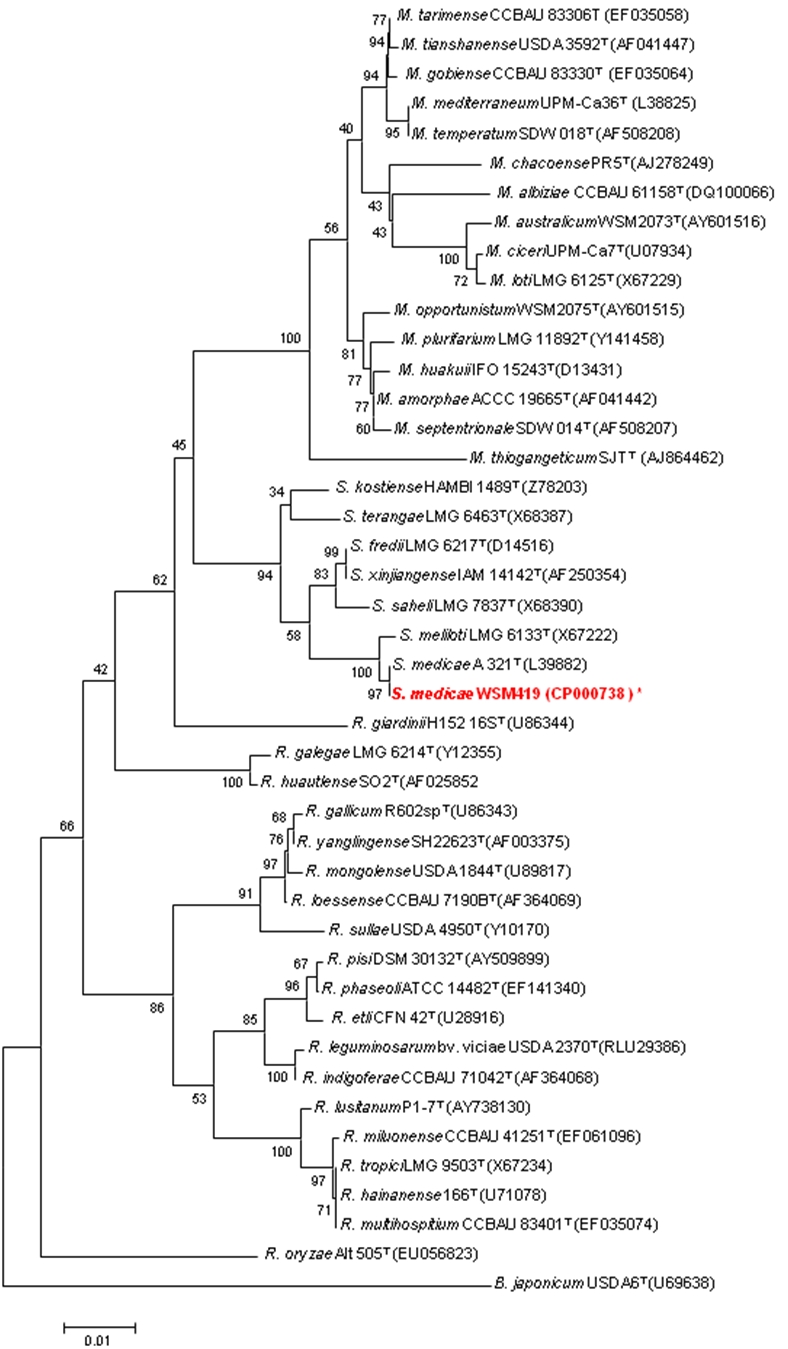
Phylogenetic tree showing the relationships of E. medicae strain WSM419 to type strains in the Rhizobiaceae based on aligned sequences of the 16S rRNA gene (1,440 bp internal region). All sites were informative and there were no gap-containing sites. Phylogenetic analyses were performed using MEGA, version 3.1 [34]. Kimura two-parameter distances were derived from the aligned sequences [35] and a bootstrap analysis [36] as performed with 500 replicates in order to construct a consensus unrooted tree using the neighbor-joining method [37] for each gene alignment separately. Genera in this tree include Bradyrhizobium (B); Mesorhizobium (M); Rhizobium (R); Ensifer (Sinorhizobium) (S). Type strains are indicated with a superscript T. Strains with a genome sequencing project registered in GOLD [31] are in bold red print. Published genomes are designated with an asterisk.
