Figure 3.
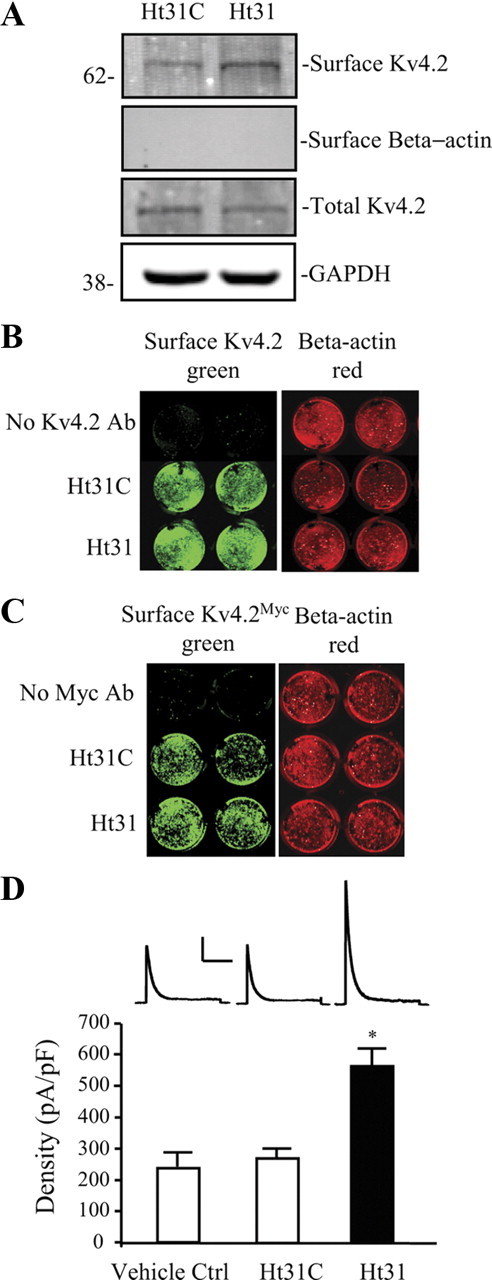
Surface Kv4.2 expression is enhanced after disrupting PKA anchoring in hippocampal neurons. DIV14 cultured embryonic day 18 (E18) rat hippocampal neurons were treated with Ht31 control peptide or Ht31 peptide (10 μm, 15 min). A, Surface proteins were labeled with NHS-SS-Biotin in a biotinylation assay and probed with mouse anti-Kv4.2 (1:2000). Surface level of endogenous Kv4.2 is significantly increased by Ht31 treatment in neurons compared with the Ht31 control. GAPDH served as a loading control. β-Actin is labeled as negative surface control. Ht31 increases surface Kv4.2 by ∼2-fold (n = 5, p < 0.05). B, C, On-cell Western assay of surface endogenous Kv4.2 (B) and overexpressed Kv4.2 by infection with Kv4.2Myc Sindbis virus (C) in hippocampal cultured neurons. The top row is control without Kv4.2 antibody labeled, the second row is treated with Ht31 control peptide (Ht31C), and the last row is treated with Ht31. Intensity levels of surface endogenous or overexpressed Kv4.2 (green) were significantly increased in wells of Ht31-treated compared with Ht31 control. The intensity levels of total β-actin (red) were not different in each well, demonstrating that equal numbers of neurons are found in each well. Data showed a significant increase in surface Kv4.2 with Ht31 treatment (n = 6, p < 0.05). D, In electrophysiological recordings from cultured hippocampal neurons, peak current density of Kv4.2-mediated currents was also significantly increased (∼2-fold) by Ht31 (n = 11, *p < 0.05) peptide application compared with Ht31 control (n = 14). Vehicle control (50 μm Tris-HCl) does not affect A-current density (n = 10). Error bars represent SEM. Calibration: 200 pA, 200 ms.
