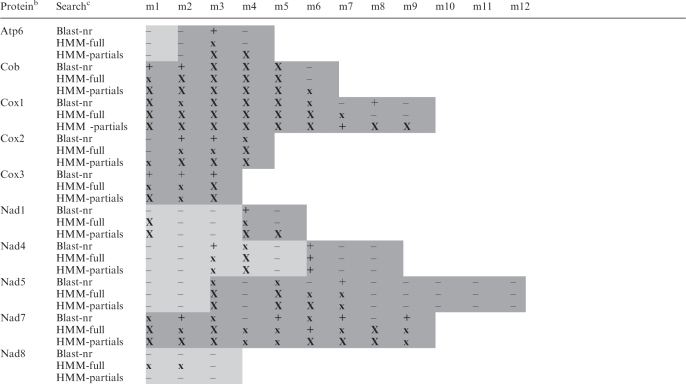
Table 3.
In silico assignment of gene modules in mtDNA sequencea
 |
|---|
aShading indicates modules that a given gene includes. Dark shading, modules for which cDNA data were obtained. X, identified module displaying a strong hit (Blast: ≤1.0e-12; HMM-full: ≤1.0e-8; HMM-partials: ≤1.0e-5). x, identified module displaying a moderate hit (Blast: between <1.0e-12 and >1.0e-5; HMM-full: >1.0e-8; HMM-partials: >1.0e-5). +, identified module displaying a marginal hit with an e-value in the range of numerous false positives (Blast: ≥1.0e-5; HMM-full: >2.0e-2; HMM-partials: >1.0e-2); true positives have been validated by the criteria described in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section. –, non-identified module by similarity search with top hits of unrelated proteins. Modules which could not be identified by the three in silico methods are likely not missing from the genomic data set (see ‘Materials and Methods’ section for coverage), but rather unrecognizable. Note that many modules have been assigned by database searches with the conceptually translated contiguous cDNA sequence, while no significant results were obtained with individual gene modules.
bProteins encoded by mtDNA. For full product names, see Table 4.
cBlast-nr, remote blastp search of proteins <14 residues long, conceptually translated in all six frames from Diplonema cassette sequences, against the non-redundant nucleotide database in GenBank. Hits to published Diplonema sequences were not considered in this table. HMM-full, search with a profile HMM, which was constructed from complete homologous proteins from non-diplonemid species, against proteins conceptually translated in all six frames from Diplonema cassette-sequences. HMM-partials, profile HMMs were constructed from protein sub-regions corresponding to modules in Diplonema mtDNA.
