Figure 3.
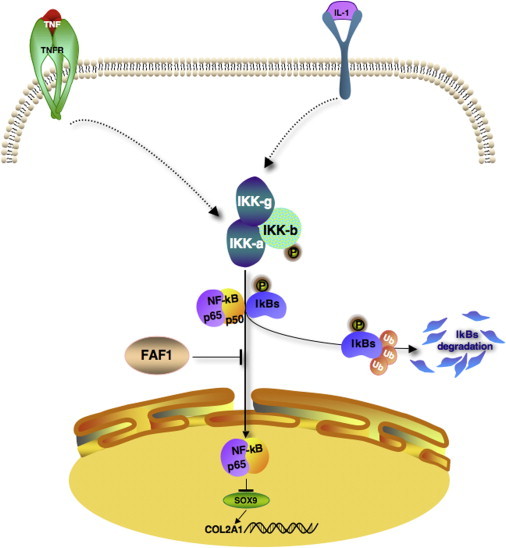
Proposed FAF1 Role in Chondrogenesis
NF-κB binds to IκB inhibitor in cytoplasm in an inactive form. In the presence of FAF1, NF-κB translocation to the nucleus is inhibited, and SOX9 and COL2A1 are normally expressed. In the absence of FAF1, upon NF-κB activation by IL-1 and TNF, subunit kinases IKK-α, -β, and -γ are activated. Phosphorylated IκB is ubiquitinated and degraded. Free NF-κB translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and inhibits expression of SOX9 and COL2A1, leading to defective chondrogenesis (e.g., CPO). Abbreviations are as follows: TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor; IL-1, interleukin-1; IκB, kappa light polypeptide [arrowheads]).
