Figs 10–18.
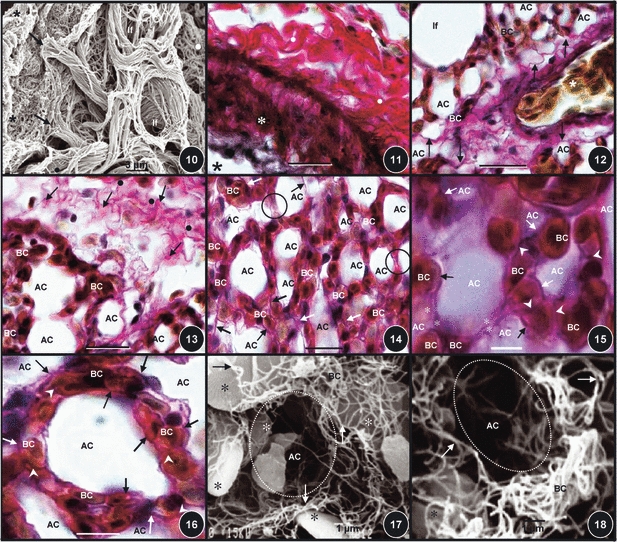
(Fig. 10) Collagen fibers of the atrial septa (star) connecting to the infundibula ones (arrows) which in turn connect to the very thin collagen fibers of the exchange tissue (dot). Scale bar: 20 mm. (Fig. 11) The wall of an interparabronchial blood vessel (asterisk) surrounded by a thick layer of collagen fibers in the tunica adventitia (dots). Star, lumen of the blood vessel. Scale bar: 20 μm. (Fig. 12) An intraparabronchial artery (star) entering the exchange tissue accompanied by collagen fibers (arrows). AC, air capillaries; BC, blood capillaries. If, infundibulum. Scale bar: 20 μm. (Fig. 13) Collagen fibers running from the interparabronchial septum (dots) into the exchange tissue (arrows). BC, blood capillaries; AC, air capillaries. Scale bar: 15 μm. (Fig. 14) Diffuse organization of collagen fibers (arrows) in the exchange tissue. BC, blood capillaries; AC, air capillaries. Circled areas, sites where air capillaries lie adjacent to each other and where collagen fibers accompany the epithelial cell extensions. Scale bar: 10 μm. (Fig. 15) Collagen fibers that are located in the blood–gas barrier (arrows) and in the epithelial cell extensions (stars) [areas that separate the air capillaries (AC) while connecting the blood capillaries (BC)], and also in the areas where BCs lie next to each other (arrowheads). Scale bar: 8 μm. (Fig. 16) Collagen fibers that are associated with air capillaries. Arrows, collagen fibers in the blood–gas barrier; arrowheads, collagen fibers in sites where blood capillaries lie adjacent to each other; BC, blood capillaries; AC, air capillaries. Scale bar: 5 μm. (Figs 17, 18) Collagen fiber network in the exchange tissue (arrows). The red blood cells which were spared during the digestion process are shown by stars. AC and circled areas, air capillaries; BC, blood capillaries (BC). Scale bars: (Fig. 17) 10 μm, (Fig, 18) 10 μm.
