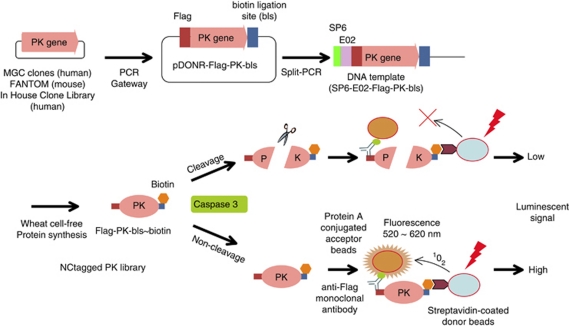
Figure 1.
Schematics of the DNA template construction and the CASP3-substrate-screening assay. Protein kinase (PK) genes were obtained from the human MGC and mouse FANTOM libraries, and from a library of PK genes that we had cloned. The PK genes were PCR amplified with the Flag and the biotin ligation site (bls) tags added to the upstream and downstream ends, respectively. The modified genes were each inserted into a Gateway pDONR221 vector (pDONR-Flag-PK-bls) and DNA templates (SP6-E02-Flag-PK-bls) were constructed by split-primer PCR and then expressed in the wheat cell-free protein synthesis system that included biotin ligase and -biotin to give Flag-PK-bls∼biotin constructs. The Flag and biotin tags were bound to protein A-conjugated acceptor beads via an anti-Flag antibody and streptavidin-conjugated donor beads, respectively. An intact complex luminesced strongly, whereas after CASP3 cleavage and dissociation of the protein fragments, the luminescence was abolished or reduced