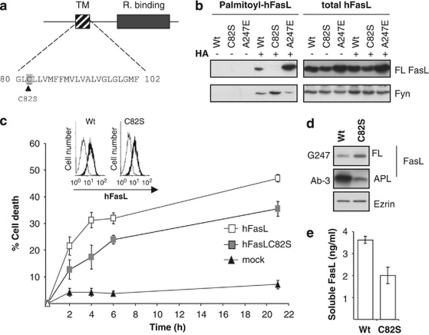
Figure 3.
Palmitoylation of hFasL is required for optimal hFasL processing and cytotoxic activity. (a) Diagram of the hFasL transmembrane domain, highlighting the proposed palmitoylation site at aa 82, which we mutated to serine. (b) WSU cells stably transfected with constructs encoding for hFasL, hFasLC82S or hFasLA247E were subjected to an acyl-biotinyl exchange protocol as described in Materials and Methods. Specificity of the experiment was controlled by omitting the hydroxylamine (HA) treatment and Fyn was used as an internal control for reaction efficiency. (c) JH6.2 cells were co-cultured for the indicated time points with WSU cells stably transfected with hFasL, hFasLC82S or mock. Cell death was then quantified by flow cytometric analysis of the subG1 population of propidium iodide-stained ethanol-fixed cells. The graph represents the average of four independent experiments with error bars indicating the S.D. The level of expression of wild-type hFasL or hFasLC82S at the cell surface of WSU transfected cells was comparable (see the inset). (d) Cell lysates of WSU cells stably transfected with constructs encoding for hFasL, hFasLC82S or mock transfected were analyzed by western blotting. (e) Levels of soluble FasL were measured in the supernatant of WSU cells stably transfected with wild-type hFasL or hFasLC82S. The graph represents the average of two independent experiments with error bars indicating the S.D.