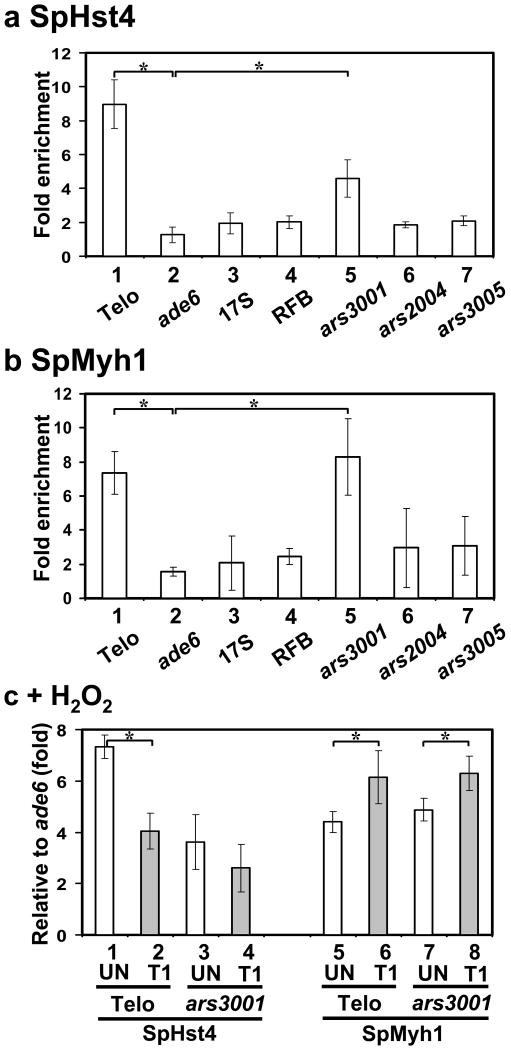
Fig. 5.
The associations of SpHst4 and SpMyh1 at telomeres and ars3001 of the rDNA repeat are altered following oxidative stress. (a) S. pombe cells (Hu1500) were subjected to ChIP assay with c-Myc antibody to precipitate SpHst4-Myc associated DNA. Precipitated DNA (IP) samples were amplified with primers listed in Table S2 by quantitative PCR (qPCR). Enrichment (n-fold) was calculated according to the formula 2ΔCt-ΔCtControl, in which ΔCt is the difference between the number of cycles required to go above background in input and IP samples. The control is the sample with beads only. Statistical significances between telomeres (Telo) and ars3001 relative to ade6+ are indicated with stars. (b) ChIP was performed similarly to (a) except that SpMyh1 antibody was used to precipitate SpMyh1 associated DNA. (c) ChIP was performed similarly to (a) and (b) except that Hu1500 cells was treated with 5 mM H2O2 for 30 min and then recovered for one hour (T1) or left untreated (UN). c-Myc antibody (columns 1-4) and SpMyh1 antibody (columns 5-8) were used to precipitate SpHst4 and SpMyh1, respectively, associated DNA. Fold enrichment at Telo and ars3001 was calculated relative to ade6+. Statistical significance (P < 0.02) between wild-type and hst4Δ is indicated with a star.