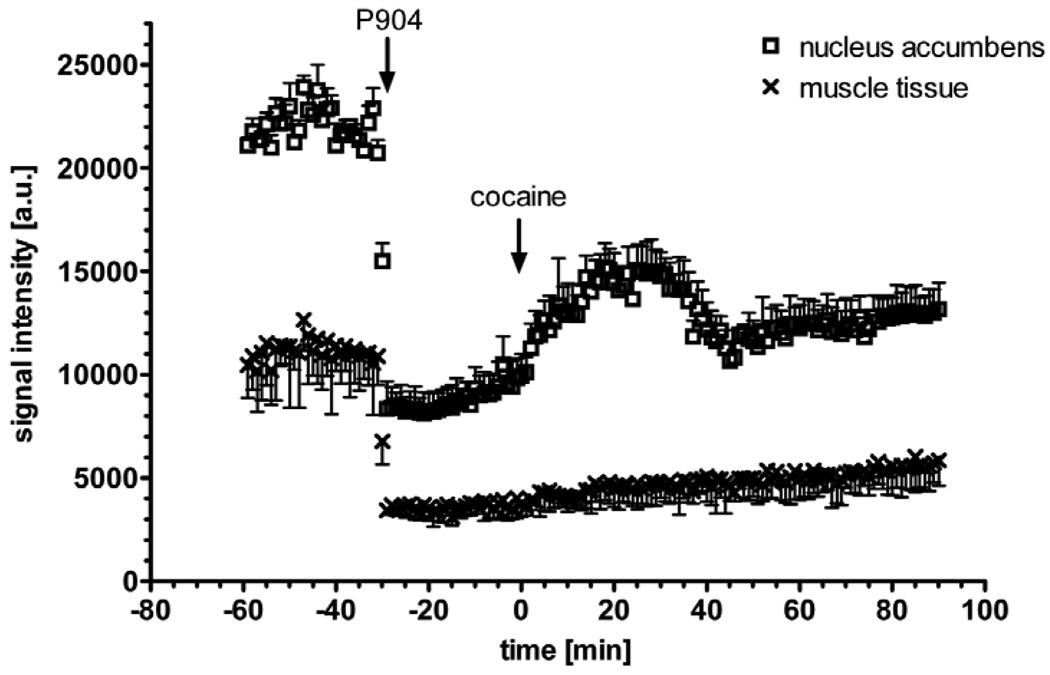
Figure 2.
Effect of IP cocaine on the signal time course in cerebral (nucleus accumbens, open symbols) and in extra-cerebral tissue (muscle, closed symbols). Injection of 25 mg/kg P904 IV at t = −30 min (left arrow) yields a 62.5% signal drop in nucleus accumbens (4.06 mm3) and 69.1% signal drop in muscle (9.58 mm3) at TE = 9.5 ms. The second arrow indicates the IP injection of cocaine (30 mg/kg), which leads to a signal increase in the cerebral tissue corresponding to a CBV decrease. The error bars show the standard deviation of the signal within the ROI in a single mouse. This is a typical signal time course prior to detrending.