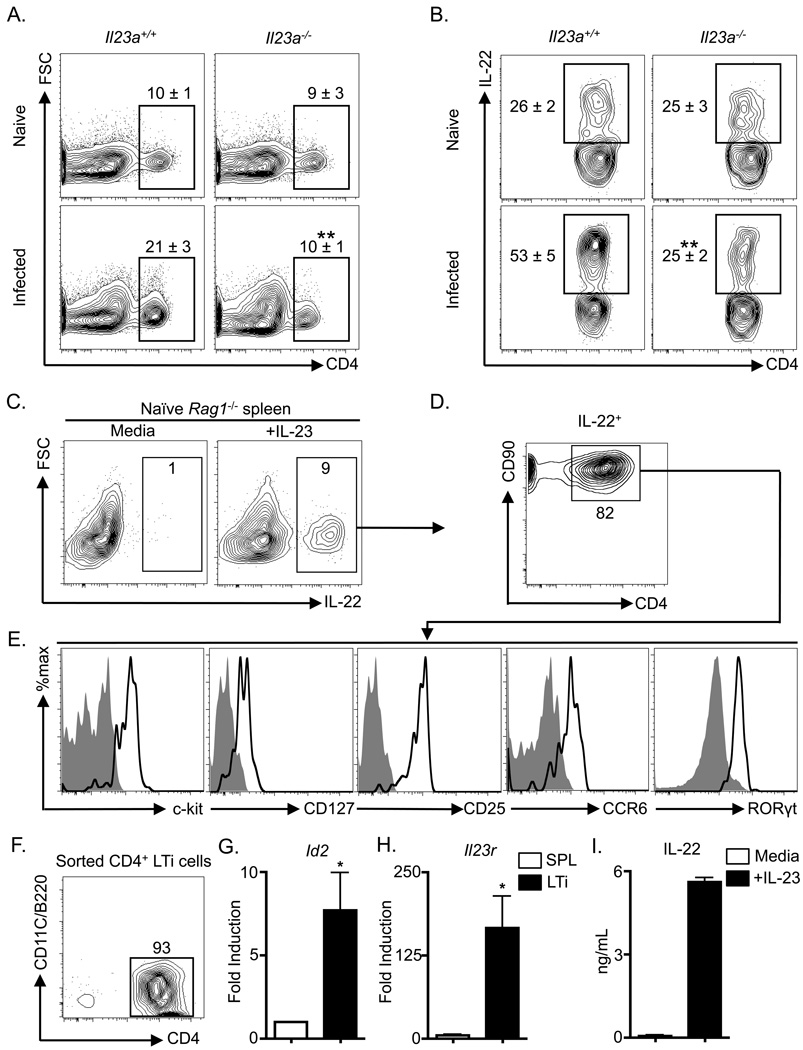
Figure 3. Citrobacter rodentium-induced adult CD4+ LTi cell responses are dependent on IL-23.
Il23a+/+ and Il23a−/− mice were infected with C. rodentium on day 0 and sacrificed on day 8. (A) Frequency of CD4+ LTi cells in the mLN of naïve and infected mice. Populations are gated on live CD3− CD5− CD90+ CD4+ cells. (B) Frequency of ex vivo stimulated IL-22+ CD4+ LTi cells in the mLN. Populations are gated on live CD3− CD5− CD90+ CD4+ cells. All data are representative of 2 or more independent experiments with a minimum of 3–4 mice per group. Naïve Rag1−/− mouse splenocytes were cultured overnight with or without rIL-23. (C) Frequency of IL-22+ cells with gating on live cells. (D) Frequency of CD90+ CD4+ cells in the IL-22+ gated population of (C). (E) The IL-22+ CD90+ CD4+ population of (D) was stained with c-kit, CD127, CD25, CCR6 and RORγt antibodies (bold black lines) and corresponding isotype and negative control antibodies (solid grey histograms). (F) CD4+ LTi cells were purified from naïve Rag1−/− splenocytes and stained with CD4, CD11c and B220 antibodies. Fold induction of (G) Id2 and (H) Il23r mRNA in purified CD4+ LTi cells relative to total unfractionated Rag1−/− splenocytes (SPL). (I) IL-22 protein in culture supernatants from purified CD4+ LTi cells stimulated in the presence or absence of rIL-23. All in vitro data are representative of 2 or more independent experiments with a minimum of 2–3 replicate wells. Data shown are the mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01. See Figure S2 for additional data.