Figure 1. Asf1 Affects Heterochromatic Silencing in S. pombe.
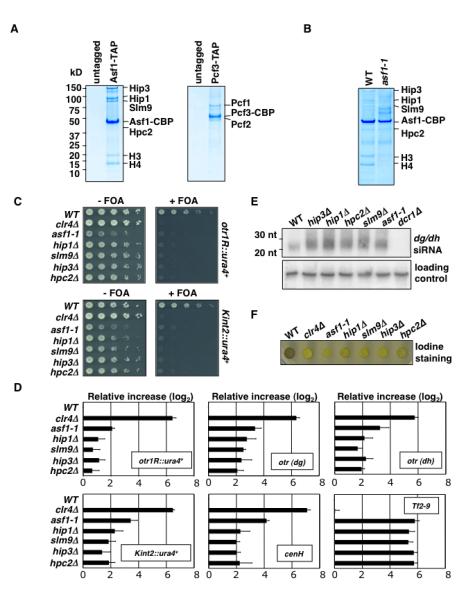
(A) Purification of Asf1 and CAF-1. SDS-PAGE followed by coomassie blue staining of untagged control, Asf1-TAP and Pcf3-TAP purification. Purified fractions were subjected to tandem MS (LC-MS/MS). (B) Coomassie blue staining of Asf1-TAP purification from wild type and asf1-1 mutant. (C) Heterochromatic silencing of reporter genes inserted at pericentromeric repeats (otr1R::ura4+) and silent mat locus (Kint2::ura4+). Serial dilution plating on counter-selective fluoroorotic acid (FOA) medium used to assay ura4+ expression. (D) asf1-1 affects silencing of heterochromatic repeats and Tf2. qPCR was used to assay expression of indicated loci. Values shown were normalized to act1+ expression. Error bars indicate standard deviations from three independent experiments. (E) Defective TGS in mutants results in elevated levels of dg/dh siRNAs. siRNAs levels were analyzed by northern blot. (F) Mutations in Asf1/HIRA impair mating-type switching. In contrast to colonies formed by wild-type homothallic (h90) cells, which switch mating-type efficiently and stain dark with iodine vapors, colonies formed by h90 asf1 and HIRA mutants stain light, owing to defective mating-type switching. Δclr4 is shown as a control.
