Figure 2. Swi6-dependent and –independent Localization of Histone Chaperone.
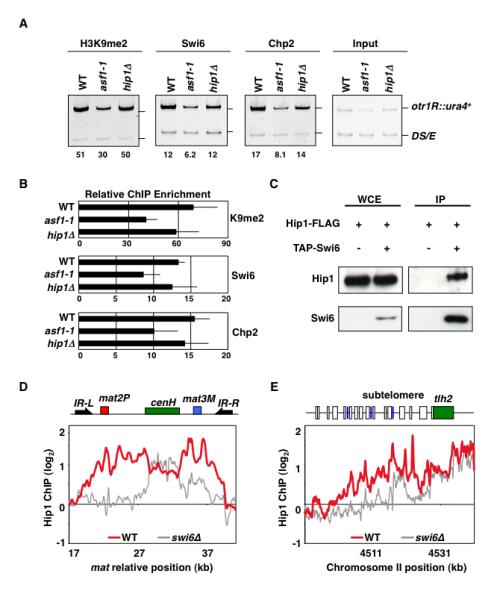
(A) asf1-1 and hip1Δ maintain heterochromatin signatures of H3K9me, Swi6, and Chp2. Strains carrying otr1R::ura4+ and ura4DS/E minigene at the endogenous locus were used to perform ChIP. Intensities of bands representing otr1R::ura4+ and ura4DS/E in ChIP and input lanes were used to calculate relative fold enrichment values shown. (B) qPCR using DNA isolated from either immunoprecipitated chromatin or input DNA was used to calculate relative fold enrichment at centromeres. Error bars indicate standard deviations from three independent experiments. (C) Swi6 interacts with Hip1. Strains expressing functional FLAG-epitope tagged Hip1 (Hip1-FLAG) and/or TAP-tagged Swi6 (TAP-Swi6) were used to perform purification. Purified fractions from untagged or TAP-tagged Swi6 samples were analyzed by western blotting using anti-FLAG antibody. (D and E) Hip1 localization across silent mat locus and subtelomeres requires Swi6. ChIP-chip was used to determine Hip1-FLAG distribution in wild type and swi6Δ cells. At silent mat locus, heterochromatic domain containing mat2 and mat3 loci as well as cenH is surrounded by IR-L and IR-R boundary elements. The subtelomeric region of right arm of chromosome II includes tlh2 gene sharing homology to dh, LTRs (blue boxes) and ORFs (open boxes).
