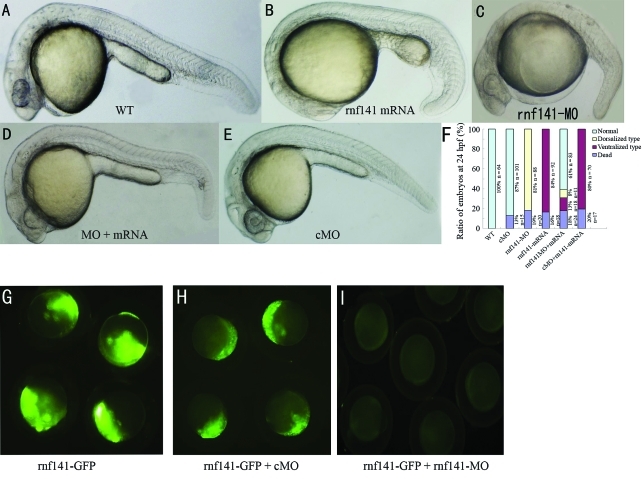
Figure 4.
Knockdown and overexpression analysis of rnf141. All images are lateral views of live embryos at 24 hpf, anterior is to the left. (A) Wild-type embryo. (B) Injection with 200 pg rnf141 mRNA resulted in enlargement of the yolk sac, in addition an extension and broadening of caudal ventral fin. (C) Injection with 12 ng rnf141-MO led to caudal ventral fin loss of and yolk sac extension. (D) Coinjection with 100 pg rnf141 mRNA and 12 ng rnf141-MO resulted in a normal morphology. (E) Injection with 15 ng of a control morpholino, which differed from rnf141-MO in five mismatched nucleotides, did not show visible developmental defects. (F) The ratios of embryos showing different phenotype in experiments represented in A-E. Data were averaged from three independent experiments and expressed as means and standard deviations. The numbers of analysed embryos are indicated beneath each bar. (G-I) Live embryos at the shield stage, (G) embryos injected with 100 pg prnf141-GFP DNA. (H) Embryos injected with 100 pg prnf141-GFP DNA and 12 ng rnf141-5mis-MO. (I) embryos injected with 100 pg prnf141-GFP DNA and 12 ng rnf141-MO.