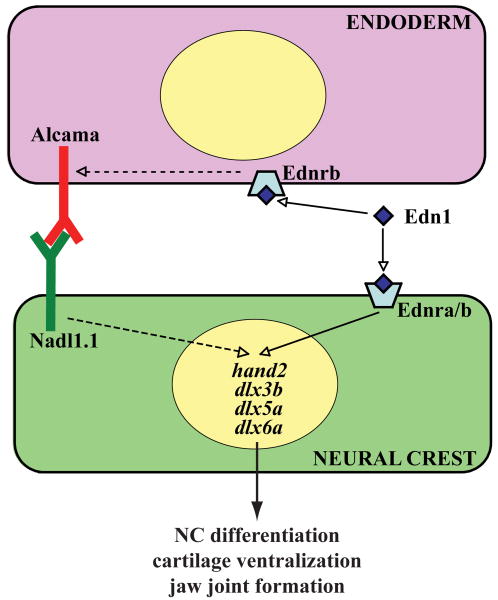
Fig. 8. Model demonstrating how Alcama mediates Edn1 signaling and NC differentiation.
Previous data has supported the model that Edn1 peptide binds to its G-protein coupled receptor on NC to turn on transcription of NC genes. We propose a parallel pathway by which Edn1 signaling stabilizes Alcama protein in endodermal cells. Alcama, in turn, binds to Nadl1.1 in NC and regulates NC differentiation.