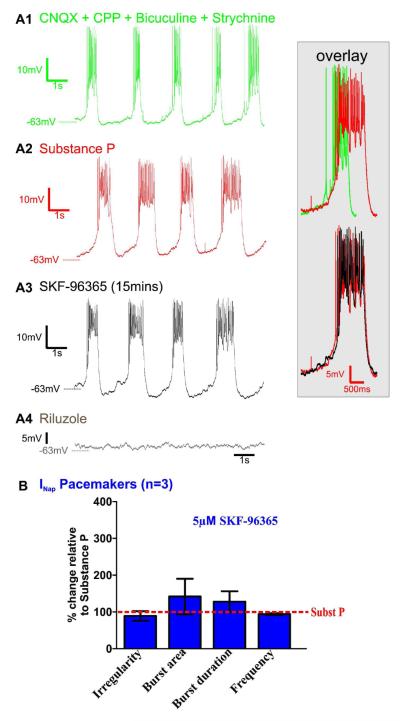
Figure 8. Persistent sodium current (INaP) pacemaking is not TRPC channel dependent.
A1) INaP-dependent pacemaker neuron activity recorded while bath-applying a mixture of CNQX, CPP, bicuculine, strychnine. A2) Bath application of SubP (0.1μM, 20mins.) enhances INaP)-dependent pacemaker activity bursting properties (green/red overlay). A3) In the presence of SubP, subsequent bath application of SKF-96365 (5μM) 15mins),, does not block SubP-enhanced rhythmic bursting of INaP-dependent pacemakers (red/black overlay). A4) As expected, INaP-dependent pacemaker bursting properties are abolished within 10mins. following additionally applying riluzole 10μM. B) In the presence of SubP, the burst irregularity, the burst area, the burst duration or the frequency were not affected by subsequently adding SKF-96365 (statistical tests were made on raw data).