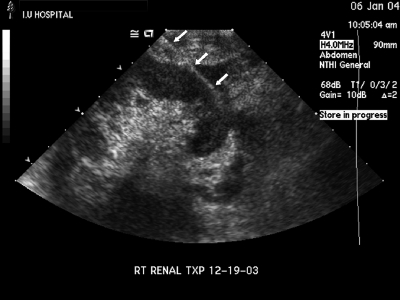
Figure 2.
The entire needle tract from the skin to the needle tip is demonstrated (arrowheads). The tract traverses the hypoechoic peripheral rind of renal cortex. The hyperechoic renal sinus complex situated more centrally is completely avoided. The figure also demonstrates the greater thickness of cortex available at the renal poles. An oblique needle approach as depicted in this figure traverses the greatest thickness of the cortex, thus maximizing the diagnostic yield, and at the same time avoids the larger vessels situated in the renal sinus complex.