Figure 1.
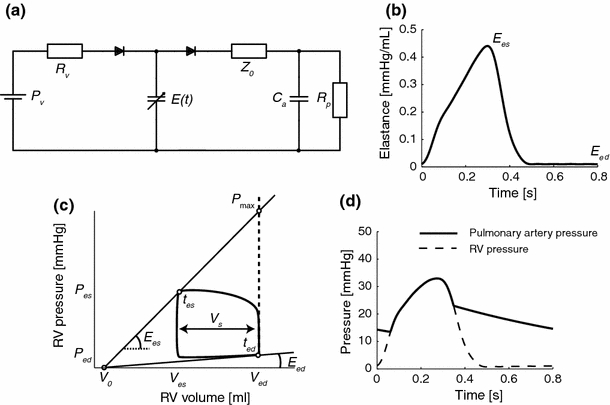
(a) Arterial-ventricular interaction model. The arterial system is modeled by a three-element windkessel model, consisting of characteristic impedance (Z 0), peripheral vascular resistance (R p) and arterial compliance (C a). The heart is modeled using a time-varying elastance model, with elastance function constructed using a normalized elastance curve18 as depicted in (b). A pressure–volume loop with the major ventricular parameters is shown in (c). Examples of simulated pulmonary artery pressure P a(t) and right ventricular pressure P RV(t) are shown in (d). E es = end-systolic elastance; E ed = end-diastolic elastance; V 0 = intercept volume; P v = venous filling pressure; R v = venous resistance; t es = time to reach end-systolic elastance; t ed = time to reach end-diastolic elastance; V s = stroke volume; P max = maximum isovolumic pressure
