Fig. 1.
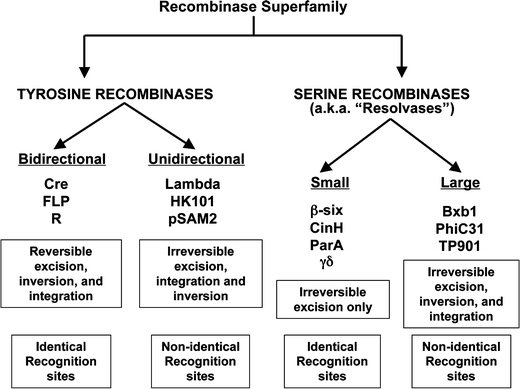
Diagram of the recombinase super family. The two major families are divided based on the active amino acid of the catalytic domain, either a tyrosine or a serine. The tyrosine family can be divided into members that utilize identical and non-identical recognition sites. Those depend on identical recognition sites are the bidirectional tyrosine and are reversible in action while the unidirectional tyrosine that utilize non-identical sites are irreversible. Members of the serine family are irreversible in action but can be further divided into “large” (~60 kDa) or “small” (~23 kDa) families based on enzyme size. While the “small’ members utilized identical recognition sites, they appear only capable of excision due to topological constraints. The “large” serine is efficient at excision, integration and inversion. Examples of each subfamily are listed and their mode of action and the nature of the recognition sites are shown
