Fig. 4.
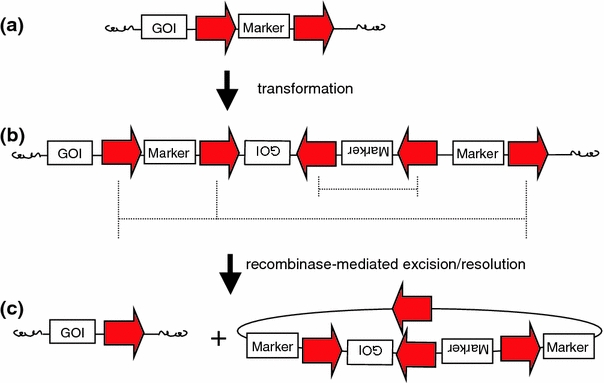
Schematic representation of a recombinase-mediated resolution event. This technique uses the recombinases’ capacity to excise DNA from between any two directly oriented recognition sites (red arrows) thereby removing the intervening or ‘complexed’ DNA from the genome. a The initial construct used for transformation. b Complex transgene integration. Dotted line designates all possible excision events mediated by directly oriented recognition sites. c Transgene resolution to a single recognition site in the genome and non-replicating circular fragment. DNA fragments present without flanking recognition sites will not be removed. The recombinase can be provided in cis or in trans—not shown. All possible excision products—not shown
