Fig. 5.
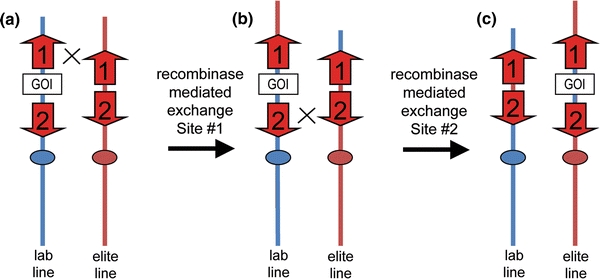
Schematic representation of a recombinase-mediated introgression event. The gene of interest (GOI) is flanked by oppositely oriented recombinase recognition sites (red arrows; #s 1 and 2). Inverted recognition sites prevent unwanted DNA excision. The recombination event targets the DNA between the associated recognition sites of different chromosomes. Two recombination events are needed to break the linkage drag associated with tradition breeding techniques. a The first event produces a transposition between the different chromosomes of the lab and elite lines (see recognition sites; red arrows # 1). b The second recombination event reverses the transposition (see recognition sites; red arrows # 2) and c leaves the transgene in the elite line. In theory this technique could be used to stack genes directly from laboratory lines into elite lines
