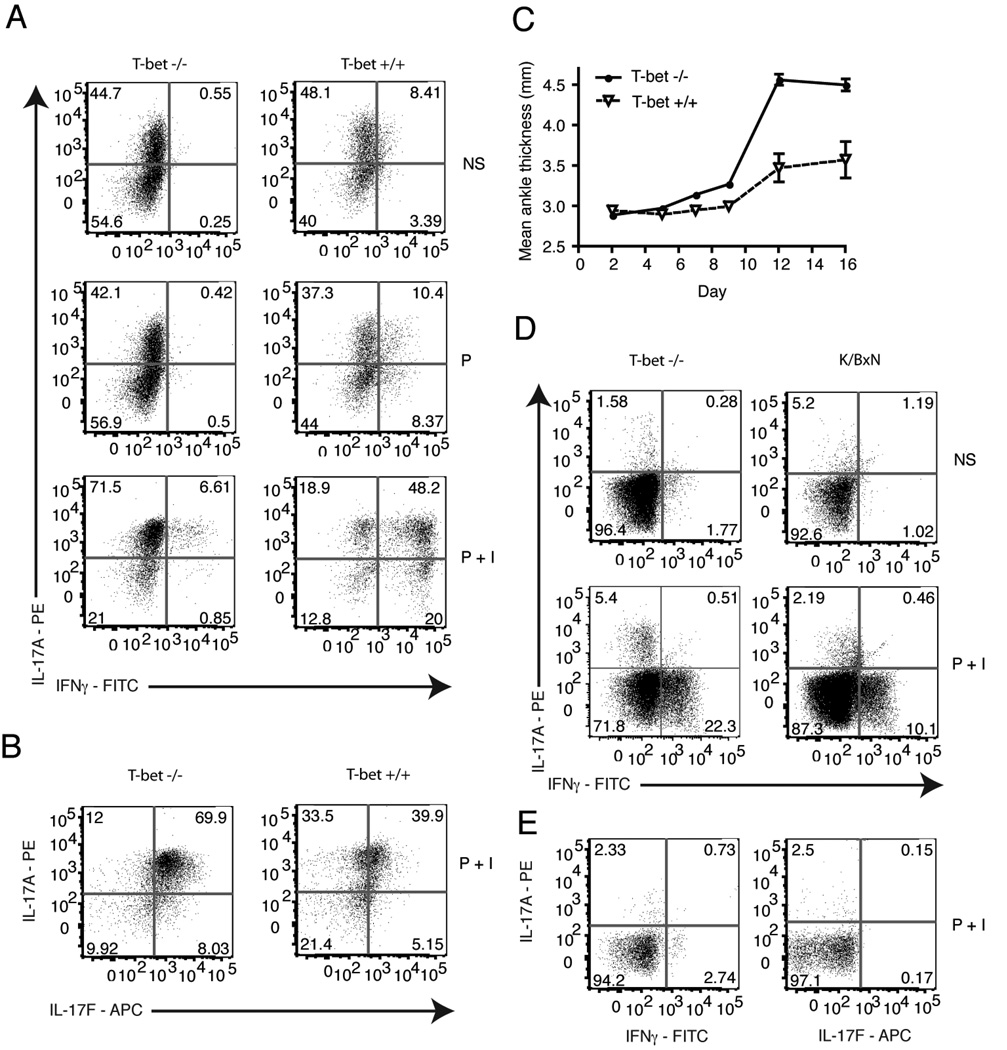
Figure 5.
IFNγ is suppressed in Th17 polarized T cells from KRN/T-bet−/− mice in vitro but not in vivo. Naive KRN/T-bet−/− T cells were cultured for 3 weeks under Th17 polarizing conditions using B6.G7 splenocytes as antigen presenting cells. a, Polarized cells were stimulated for 4 h with PMA or PMA + ionomycin. T cells were gated on TCR Vβ6+ live cells and stained for IL-17A and IFNγ, or b, IL-17A and IL-17F. c, On day 0, 10×106 KRN/T-bet−/− or KRN (T-bet+/+) Th17 polarized cells were injected i.v. into B6.TCR.Cα−/−H-2b/g7 mice and the thickness of both rear ankles was measured as a indication of arthritis (n= 9 KRN/T-bet−/− mice and 3 KRN mice). Results are representative of two independent experiments. Open symbols, KRN/T-bet+/+. Filled symbols, KRN/T-bet−/−. d, On day 16 popliteal lymph nodes were harvested and cells stimulated for 4 h with PMA + ionomycin. T cells were gated on live Vβ6+ cells and stained for intracellular IL-17A and IFNγ. Results are representative of 13 mice. e, On day 1 popliteal lymph nodes were harvested and cells stimulated for 4 h with PMA + ionomycin. T cells were gated on live Vβ6+ cells and stained for intracellular IL-17A, IFNγ, and IL-17F. Results are representative of one mouse. NS, no stimulation. P, PMA. P+I, PMA + ionomycin.