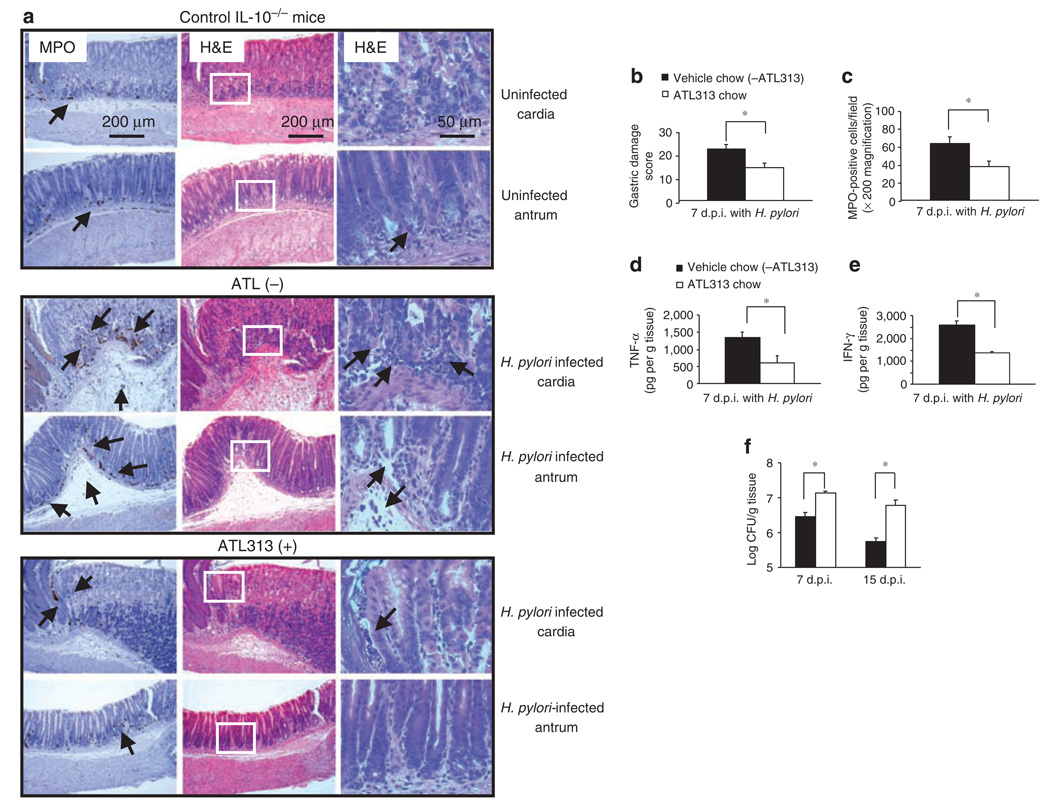
Figure 8.
Oral administration of an A2AAR agonist in Helicobacter pylori-infected IL-10−/− mice reduces gastric inflammation but increases bacterial load. IL-10-deficient mice were infected as described in Figure 7. All mice were given either vehicle control chow (ATL313(−), n = 4) or ATL313 chow (ATL313(+), n = 4) for 1 week before infection and continued until killing. Mice were killed 7(7d.p.i.) or 15 days (15d.p.i.) later, and gastric tissue (each longitudinal section) was processed for histology, MPO staining, mucosal cytokine expression, and H. pylori colonization by colony count. (a) Myeloperoxidase (MPO) (left panel) and H&E stained (two right panels with inset from center panel shown at higher magnification in the outer right panel) of gastric sections from representative uninfected IL-10−/− (upper panels), and infected IL-10−/− without (middle panels) or with ATL313 chow-treated mice (lower panels). Arrows indicate MPO-expressing cells (original magnification of × 100). Some scattered mononuclear cells (MNCs) and MPO-positive granulocytes can be seen in the submucosa and lamina propria, with no abnormal thickening of the gastric wall of uninfected control IL-10-deficient mice. Severe gastritis with dense MNC infiltration and diffuse MPO-positive granulocytes in the submucosa and mucosa of the untreated infected mice in both cardia and antral regions. A concomitant hyperplasia with widespread thickening of the gastric wall as well as of gastric atrophy can be observed. ATL313-treated mice are almost normal with few inflammatory cells infiltration. (b) Histological scoring of gastritis, (c) quantitative expression of MPO-positive cells expressed per field, and (d) mucosal TNF-α, and (e), IFN-γ production in gastric tissue of in H. pylori-infected IL-10-deficient mice without or with ATL313 treatment. (f) H. pylori colonization in gastric tissue measured by colony count on days 7 and 15 after infection with same treatment as mentioned earlier. Data are mean±s.e.m. from one experiment with four mice per group that was carried out at least twice with similar results. * Significant difference (P < 0.05) between the untreated and treated mice.