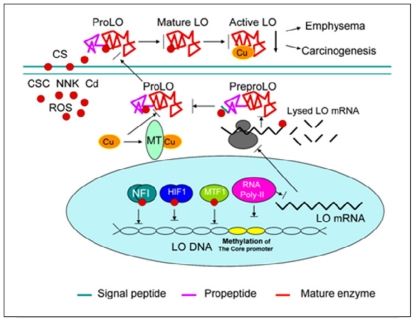
Figure 6.
CS perturbs LO at transcriptional, translational and catalytic levels. At the promoter level, CS interferes with the interaction of redox-sensitive transcription factors such as NFI, HIF1, MTF-1 with corresponding cis-elements and induces methylation of CpG at the core promoter region inhibiting the initiation of LO gene transcription. At the mRNA levels, CS inhibition of both the synthesis and the stability of LO transcripts leads to decreased levels of steady-state LO mRNA. At the protein level, CS suppresses synthesis and processing of the preproLO such as signal peptide cleavage, and Cu binding to the proLO due to elevation of cellular thiols, resulting in reduction of the ProLO secretion to the ECM. At the catalytic levels mature apoLO without Cu cofactor binding exhibits the defect in enzyme activity. Thus, CS inhibition of the LO gene expression at multiple levels collectively contributes to decreased levels of the mature LO in the lung ECM favoring emphysema pathogenesis and carcinogenesis in the lung.