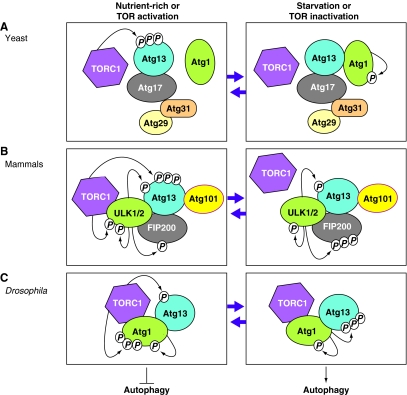
Fig. 2.
Dynamics of Atg1 complexes upon autophagy induction in different eukaryotes. (A) In yeast, under nutrient-rich conditions, the active TOR complex 1 (TORC1) hyperphosphorylates Atg13 (Kamada et al., 2010). This prevents the association of Atg1 with Atg13, which is bound to Atg17, Atg31 and Atg29, leading to inhibition of autophagy induction. Under starvation conditions when TORC1 is inactivated, Atg13 is no longer phosphorylated by TORC1, whereas Atg1 is autophosphorylated, leading to the association of Atg1 with the complex between Atg13, Atg17, Atg31 and Atg29, and subsequent autophagy induction (Cebollero and Reggiori, 2009; Chang and Neufeld, 2010; Kamada et al., 2010; Nakatogawa et al., 2009). (B) In contrast to yeast, mammalian ULK (ULK1 or ULK2, the homologs of yeast Atg1) forms a stable complex with mammalian Atg13, FIP200 (a putative counterpart of yeast Atg17) and Atg101 (an Atg13-binding protein), irrespective of TORC1 activation. Under nutrient-rich conditions, the active TORC1 associates with the ULK complex (ULK1 (or ULK2)–Atg13–FIP200-Atg101), phosphorylates ULK1 (or ULK2) and hyperphosphorylates Atg13, which inhibits the kinase activity of ULK1 (or ULK2) and thus blocks autophagy induction. Under starvation conditions when TORC1 is inactivated, TORC1 dissociates from the ULK complex, preventing phosphorylation of Atg13 and ULK1 (or ULK2) by TORC1 and leading to autophagy induction, whereas ULK1 (or ULK2) still phosphorylates Atg13 and itself, and hyperphosphorylates FIP200 (Chang and Neufeld, 2010; Mizushima, 2010; Yang and Klionsky, 2010). (C) Similar to the situation in mammals, in Drosophila Atg1 forms a complex with Atg13 irrespective of TORC1 activation (Chang and Neufeld, 2010). Under nutrient-rich conditions, the active TORC1 phosphorylates Atg13 and hyperphosphorylates Atg1, leading to the inhibition of autophagy induction. Under starvation conditions, when TORC1 is inactivated, Atg1 and Atg13 are no longer phosphorylated by TORC1, whereas Atg1 still phosphorylates itself and hyperphosphorylates Atg13, leading to autophagy induction. Figure modified from Chang and Neufeld (Chang and Neufeld, 2010) with permission.