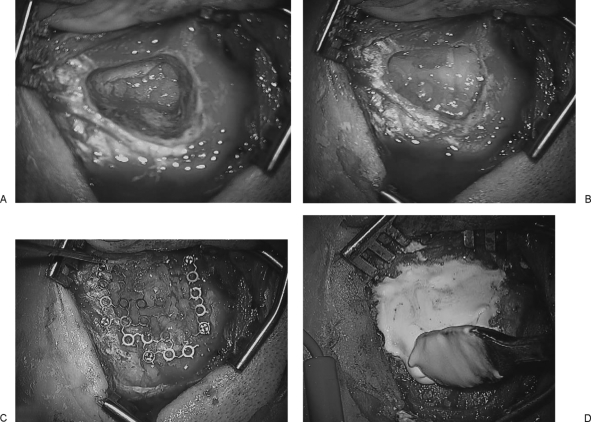
Figure 1.
Temporalis fascia is placed to cover the dural defect in the internal auditory canal and posterior fossa and sealed with fibrin glue. Bone wax is placed over the posterior epitympanum to prevent cerebrospinal fluid–middle ear communication (A). Abdominal fat is placed in the mastoid and labyrinthine defect (B). Titanium mesh is secured in the mastoid cortex with self-tapping screws, and the mesh is then bowed medially to compress the fat (C). Hydroxyapatite cement is spread over the mesh and contoured to the edges of the cortical bone (D).