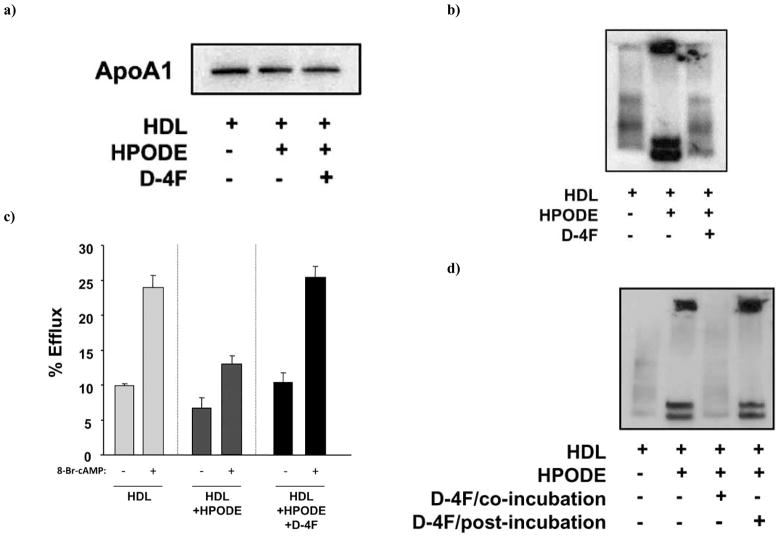
Fig. 6.
4F prevents the HPODE-mediated conversion of normal HDL into proinflammatory HDL. Human HDL (5ug HDL-cholesterol/ml) was incubated alone, or with 0.5 μg/ml of 13(S)-HPODE, or with 0.5 μg/ml of 13(S)-HPODE and 0.5 μg/ml of D-4F for 30 min and subjected to a) SDS-PAGE analysis or b) native-PAGE analysis. The gels were then subjected to Western analysis with anti-human apoA-I antibody. c) After the in vitro incubation, HDL was added to RAW264.7 macrophages and cholesterol efflux was determined as described in Materials and Methods in the presence or absence of 8-Bromo-cAMP (0.1mM) pretreatment to maximally stimulate the ABCA1 pathway. d) Human HDL (5 μg HDL-cholesterol/ml) was incubated alone, or with 13(S)-HPODE (0.5 μg/ml), or with 13(S)-HPODE (0.5 μg/ml) and D-4F (0.5 μg/ml) for 60 min (co-incubation), or with 13(S)-HPODE (0.5 μg/ml) for 30 min and then with D-4F (0.5 μg/ml) for 30 min (post-incubation). HDL was subjected to native-PAGE analysis and analyzed by Western with anti-human apoA-I antibody.