Figure 10.
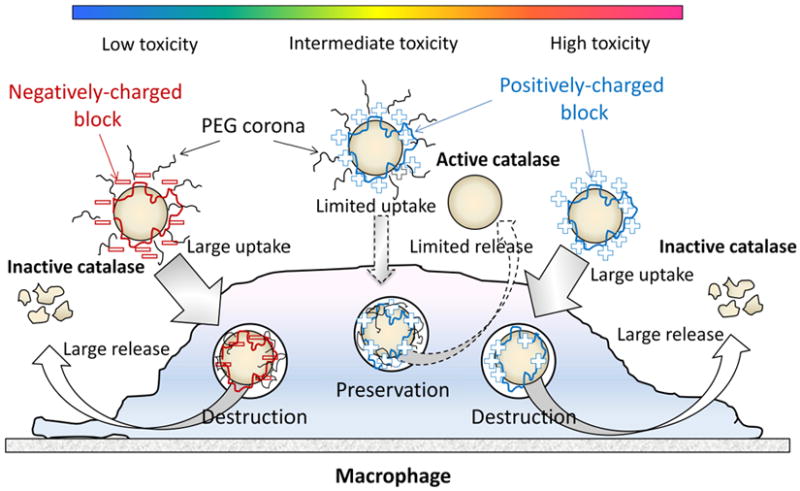
A pictoral scheme for different nanozyme structures evaluated for cell-mediated drug delivery. Three types of catalase nanozymes: Nanozyme I: contaning a negatively cherged block copolymer (with PEG) showed low toxicity, high loading capacity and sustained release from BMMs, but limited enzyme protection inside cell carriers; Nanozyme II: containing positively charged block copolymers (with PEG) showed increased cytotoxicity and low loading and release rates, but high level of nanozyme protection ; Nanozymes III: containing monopolymers (without PEG corona) showed higher loading and release rates, but low enzyme protection inside BMMs along with decreased catalase activity in cell-free system. The optimal nanozyme formulation selected from nanozyme II group is based on positively-charged block copolymers (PEI48-PEG/catalase and PL10-PEG/catalase) that demonstrate efficient protection of catalase enzymatic activity along with relatively high loading and release rates and limited cytotoxicity.
