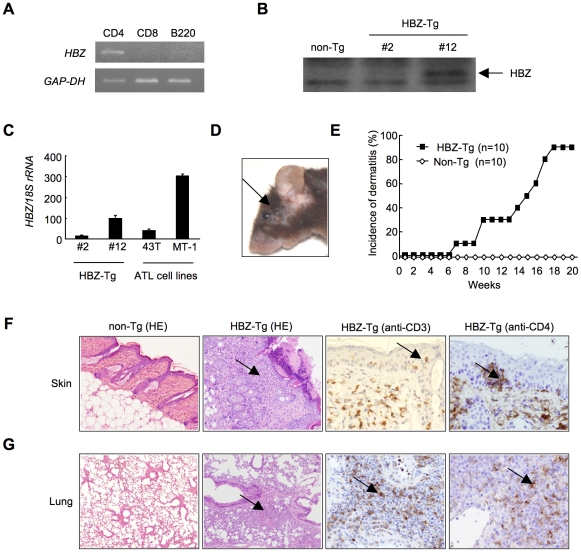
Figure 1. HBZ-Tg mice spontaneously develop inflammatory diseases in skin and lung.
(A) Cell-type specific transcription of the transgene in line 12 was confirmed by RT-PCR in each sorted cell population. (B) The expression of HBZ protein in CD4+ splenocytes was confirmed by Western blotting. (C) Transcripts of the HBZ gene in CD4+ splenocyte of HBZ-Tg mice or ATL cell lines were quantified by real time PCR. ATL-43T and MT-1 are derived from ATL cells. (D) An HBZ-Tg mouse with typical skin symptom (Arrow indicates skin lesion). (E) The incidence of dermatitis in HBZ-Tg (line 12) and non-Tg mice. (F and G) Histological findings of the skin and the lung in HBZ-Tg mice. Lymphocytes massively infiltrated the dermis and epidermis (F) and the alveolar septum (G) (Arrows present infiltration of lymphocytes). Infiltration of CD3+, CD4+ T cells into these tissues was shown by immunohistochemistry compared with non-Tg mice as control.