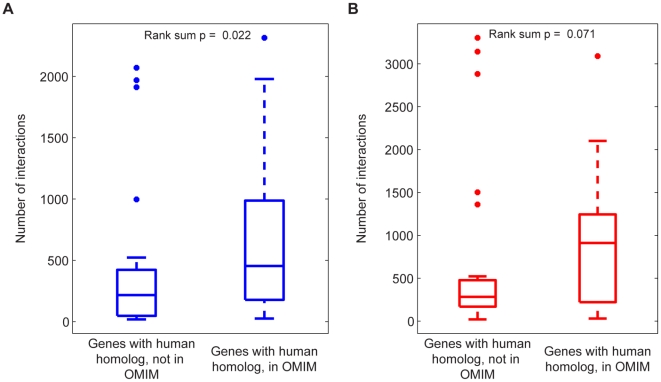
Figure 8. Disease association of genes involved in many interactions across all metabolic flux phenotypes.
The relevance of multi-phenotype epistasis to human disease was explored by comparing the total number of (A) antagonistic and (B) synergistic interactions across all phenotypes for those yeast genes with a human homolog in OMIM to those yeast genes with a human homolog that is not in OMIM. The distributions of interaction counts are displayed as box-plots with the boxes encompassing the 25th to 75th percentiles, and the line at the median value. Genes with a human homolog in OMIM have more antagonistic and synergistic interactions, with the difference for antagonistic interactions being significant at p<0.05 (Signed-rank test, p = 0.022 (antagonistic), p = 0.071 (synergistic), n1 = 30, n2 = 19).