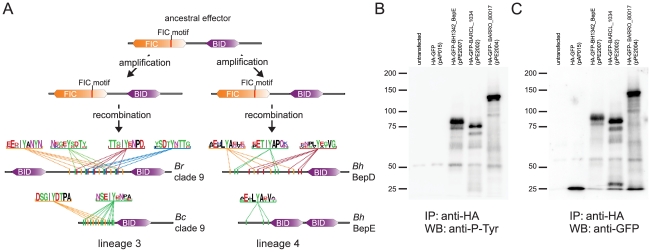
Figure 5. Parallel evolution of Bartonella effector proteins harboring tandem-repeated tyrosine motifs phosphorylated in host cells.
(A) The lineage-specific amplification of effector proteins harboring the ancestral domain structure was followed by secondary recombination events in both lineages. This resulted in the independent emergence of Beps with a derived domain structure (see also Figure S5). In silico predictions for tyrosine-phosphorylation motifs consistently detected high numbers of tandem-repeated phosphorylation sites in independently derived Beps of both lineages (here shown for two Beps of Bep clade 9 [BARRO_80017 of Br and BARCL_1034 of Bc] from lineage 3 and BepD and BepE of Bh from lineage 4). The depicted motifs were identified with NetPhos2.0 with a score ≥0.8 (for predictions of all motifs in lineage 3 see Table S4). The consensus sequence of tandem-repeated motifs (color-coded) is shown for each of the four Beps by WebLogos (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/logo.cgi). (B) and (C), Immunoprecipitation/Western blot analysis of Beps with predicted tyrosine-phosphorylation motifs ectopically expressed in HEK293T cells. Immunoprecipitations were performed with HA antibody-coated agarose beads. (B) Western blot analysis was performed with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. (C) Western blot analysis was performed with anti-GFP antibody. The tested constructs correspond to the Beps of Bep clade 9 (BARCL_1034, 70.8 kDa, and BARRO_80017, 113.1 kDa) and BepE of B. henselae (BH13420, 81.4 kDa) shown in (A). HA-GFP was used as a control (28.7 kDa).